Choosing the right career path after graduation or early in one’s professional journey can be a pivotal decision. For many aspiring professionals in finance and business, two prominent options often stand out: joining a prestigious investment bank like Goldman Sachs or diving into the dynamic world of venture capital (VC). Both paths offer unique opportunities, challenges, and learning experiences, but they cater to different skill sets and career aspirations. This article explores the key differences between starting a career at Goldman Sachs versus entering venture capital, examining factors such as skill development, work culture, long-term growth, and personal fulfillment to help you make an informed decision.
- Is Goldman Sachs or Venture Capital a Better Career Starter?
- Is venture capital a good career path?
- How hard is it to get an entry level job at Goldman Sachs?
- What pays more, VC or PE?
- Does Morgan Stanley pay more than Goldman Sachs?
- Frequently Asked Questions from Our Community
- What are the key differences between starting a career at Goldman Sachs versus Venture Capital?
- Which career path offers better long-term growth opportunities: Goldman Sachs or Venture Capital?
- How does the work-life balance compare between Goldman Sachs and Venture Capital?
- Which career path is more suitable for someone interested in entrepreneurship: Goldman Sachs or Venture Capital?
Is Goldman Sachs or Venture Capital a Better Career Starter?
1. What Are the Key Differences Between Goldman Sachs and Venture Capital?
Goldman Sachs and Venture Capital (VC) are two distinct career paths in the finance industry. Goldman Sachs is a global investment bank that offers a structured career path with roles in investment banking, asset management, and trading. On the other hand, Venture Capital focuses on investing in early-stage startups and high-growth companies, offering a more entrepreneurial and risk-oriented environment. While Goldman Sachs provides a well-defined career trajectory, VC offers exposure to innovation and startups but with less structure.
2. Which Career Path Offers Better Skill Development?
At Goldman Sachs, employees develop strong analytical, financial modeling, and client management skills due to the rigorous training programs and high-pressure environment. In contrast, Venture Capital emphasizes skills like deal sourcing, due diligence, and strategic decision-making, as professionals evaluate startups and their potential for growth. Both paths offer valuable skills, but the choice depends on whether you prefer a corporate or entrepreneurial setting.
See Also Should I Quit Venture Capital to Join Real Estate Private Equity?
Should I Quit Venture Capital to Join Real Estate Private Equity?3. How Do Compensation and Benefits Compare?
Goldman Sachs is known for its competitive compensation packages, including base salaries, bonuses, and benefits like healthcare and retirement plans. In Venture Capital, compensation can vary widely depending on the firm's size and success. While entry-level roles in VC may offer lower base salaries, the potential for carried interest (a share of investment profits) can be lucrative in the long term. However, this is often tied to the firm's performance.
4. What Are the Long-Term Career Prospects?
A career at Goldman Sachs can lead to senior roles within the bank or opportunities in other financial institutions, thanks to its prestigious reputation. In Venture Capital, long-term prospects include becoming a partner at a VC firm or transitioning to entrepreneurship. Both paths offer strong career growth, but Goldman Sachs provides more stability, while VC offers higher risk and reward potential.
5. Which Path Aligns Better with Personal Career Goals?
Choosing between Goldman Sachs and Venture Capital depends on your career aspirations. If you value stability, structured growth, and working with established companies, Goldman Sachs may be the better fit. However, if you are passionate about innovation, startups, and taking calculated risks, Venture Capital could be more fulfilling. Consider your long-term goals and preferred work environment when making this decision.
See Also Why Should I Choose Equity Crowdfunding Instead of Venture Capital
Why Should I Choose Equity Crowdfunding Instead of Venture Capital| Aspect | Goldman Sachs | Venture Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Career Structure | Structured and well-defined | Entrepreneurial and flexible |
| Skill Development | Analytical, financial modeling, client management | Deal sourcing, due diligence, strategic decision-making |
| Compensation | High base salary, bonuses, benefits | Lower base salary, potential for carried interest |
| Long-Term Prospects | Senior roles in finance, stability | Partner at VC firm, entrepreneurship, higher risk/reward |
| Alignment with Goals | Stability and corporate growth | Innovation and startup ecosystem |

Is venture capital a good career path?

What Does a Career in Venture Capital Entail?
A career in venture capital involves investing in early-stage or growth-stage companies with high potential for growth. Professionals in this field analyze business models, evaluate market opportunities, and provide strategic guidance to startups. Key responsibilities include:
- Deal sourcing: Identifying promising startups and entrepreneurs.
- Due diligence: Conducting thorough research on potential investments.
- Portfolio management: Supporting portfolio companies to achieve growth and success.
What Skills Are Required for Venture Capital?
To succeed in venture capital, individuals need a combination of technical and interpersonal skills. These include:
See Also Whats the Difference Between Growth Equity and Venture Capital
Whats the Difference Between Growth Equity and Venture Capital- Financial analysis: Ability to evaluate financial statements and projections.
- Market research: Understanding industry trends and competitive landscapes.
- Networking: Building relationships with entrepreneurs and other investors.
What Are the Pros of a Venture Capital Career?
A career in venture capital offers several advantages, such as:
- High earning potential: Successful investments can yield significant financial returns.
- Intellectual stimulation: Working with innovative startups and cutting-edge technologies.
- Influence and impact: Helping shape the future of industries and economies.
What Are the Challenges of Venture Capital?
Despite its appeal, venture capital comes with challenges, including:
- High risk: Many startups fail, leading to potential losses.
- Long hours: Extensive research and networking require significant time commitments.
- Competition: Securing top deals in a highly competitive environment.
How to Start a Career in Venture Capital?
Breaking into venture capital requires strategic planning and preparation. Steps include:
See Also Who Are the Top Venture Capital Firms in the Biotech Industry?
Who Are the Top Venture Capital Firms in the Biotech Industry?- Gain relevant experience: Work in startups, consulting, or investment banking.
- Build a network: Attend industry events and connect with professionals.
- Develop expertise: Focus on a specific industry or technology sector.
How hard is it to get an entry level job at Goldman Sachs?

What Are the Basic Requirements for an Entry-Level Job at Goldman Sachs?
Securing an entry-level position at Goldman Sachs requires meeting several rigorous criteria. The firm looks for candidates who demonstrate exceptional academic performance, relevant skills, and a strong alignment with their values. Below are the key requirements:
- Educational Background: A bachelor's degree from a top-tier university, preferably in finance, economics, business, or a related field.
- Academic Excellence: A high GPA (typically 3.7 or above) is often expected.
- Relevant Internships: Prior experience in finance, banking, or consulting through internships is highly valued.
- Technical Skills: Proficiency in financial modeling, Excel, and other analytical tools is essential.
- Soft Skills: Strong communication, teamwork, and problem-solving abilities are critical.
How Competitive Is the Application Process?
The application process for an entry-level role at Goldman Sachs is extremely competitive. The firm receives thousands of applications for a limited number of positions. Here’s what makes it challenging:
See Also Is Venture Capital or Real Estate Development More Lucrative
Is Venture Capital or Real Estate Development More Lucrative- High Volume of Applicants: Goldman Sachs attracts top talent globally, making the pool of candidates highly competitive.
- Rigorous Screening: Applications go through multiple rounds of screening, including resume reviews, online assessments, and interviews.
- Behavioral and Technical Interviews: Candidates must excel in both behavioral questions and technical assessments to advance.
- Networking Importance: Building connections with current employees or alumni can significantly improve your chances.
- Timing: Applying early and meeting deadlines is crucial, as roles are often filled quickly.
What Does the Interview Process Look Like?
The interview process at Goldman Sachs is intensive and multi-stage. It is designed to assess both technical expertise and cultural fit. Here’s an overview:
- Initial Screening: A phone or video interview to evaluate basic qualifications and interest in the role.
- Superday: A full day of interviews, typically including multiple rounds with different team members.
- Technical Questions: Candidates are tested on financial concepts, market knowledge, and problem-solving skills.
- Behavioral Questions: Questions focus on teamwork, leadership, and handling challenging situations.
- Case Studies: Some roles may require solving real-world business problems during the interview.
What Skills and Qualities Does Goldman Sachs Look For?
Goldman Sachs seeks candidates who possess a combination of technical expertise and personal qualities that align with their culture. Key attributes include:
- Analytical Thinking: The ability to analyze complex data and make informed decisions.
- Adaptability: Being able to thrive in a fast-paced and ever-changing environment.
- Leadership Potential: Demonstrating initiative and the ability to inspire others.
- Attention to Detail: Ensuring accuracy and precision in all tasks.
- Passion for Finance: A genuine interest in the financial industry and its trends.
How Can You Stand Out in the Application Process?
To stand out in the highly competitive application process, candidates need to differentiate themselves in meaningful ways. Here are some strategies:
- Tailor Your Resume: Highlight relevant experiences, skills, and achievements that align with the role.
- Prepare Thoroughly: Practice technical questions, case studies, and behavioral interviews extensively.
- Leverage Networking: Connect with Goldman Sachs employees or alumni to gain insights and referrals.
- Showcase Unique Experiences: Highlight any unique projects, internships, or extracurricular activities that demonstrate your skills.
- Demonstrate Cultural Fit: Emphasize your alignment with Goldman Sachs’ values, such as integrity and teamwork.
What pays more, VC or PE?

Understanding the Compensation Structures in VC and PE
When comparing venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE), it's essential to understand their compensation structures. Both industries offer lucrative pay, but the way earnings are structured differs significantly.
- Base Salary: In both VC and PE, professionals typically start with a competitive base salary. However, PE firms often offer higher base salaries compared to VC firms, especially at the junior levels.
- Bonuses: Bonuses in PE are generally more substantial and tied to the performance of the fund and individual deals. In VC, bonuses can be significant but are often more variable and tied to the success of portfolio companies.
- Carried Interest: This is where the real difference lies. PE professionals usually receive a larger share of carried interest, which is a percentage of the fund's profits. In VC, carried interest is also present but tends to be smaller due to the higher risk associated with early-stage investments.
Entry-Level Salaries: VC vs. PE
At the entry-level, the compensation difference between VC and PE can be quite noticeable. Here’s a breakdown:
- Analyst Roles: In PE, analysts can expect higher starting salaries, often ranging from $100,000 to $150,000, including bonuses. In VC, starting salaries are generally lower, typically between $80,000 and $120,000.
- Job Responsibilities: PE analysts often deal with more complex financial modeling and due diligence, justifying the higher pay. VC analysts, while also performing critical tasks, may focus more on market research and sourcing deals.
- Career Progression: The path to higher compensation in PE is often quicker, with promotions leading to significant salary jumps. In VC, progression can be slower, but the potential for high rewards exists if portfolio companies succeed.
Mid-Level Compensation: Associates and Principals
As professionals move up the ladder, the compensation gap between VC and PE can widen further. Here’s what to expect:
- Associate Roles: PE associates can earn between $150,000 and $250,000, including bonuses. VC associates might earn slightly less, typically between $120,000 and $200,000.
- Principal Roles: In PE, principals can command salaries upwards of $300,000, with substantial bonuses and carried interest. In VC, principals may earn slightly less, but successful exits can lead to significant payouts.
- Deal Involvement: PE principals often have more direct involvement in deal execution and portfolio management, which can lead to higher compensation. VC principals may spend more time on deal sourcing and mentoring startups.
Senior-Level Earnings: Partners and Managing Directors
At the senior level, the earnings potential in both VC and PE is substantial, but PE tends to offer higher compensation. Here’s a closer look:
- Partner Roles: PE partners can earn millions annually, with a significant portion coming from carried interest. VC partners also earn well, but the variability is higher due to the nature of startup investments.
- Managing Directors: In PE, managing directors often have the highest compensation, with earnings that can exceed $1 million annually. In VC, managing directors may earn slightly less, but successful exits can lead to substantial payouts.
- Fund Performance: The performance of the fund plays a crucial role in senior-level compensation. PE funds, with their focus on mature companies, often deliver more consistent returns, leading to higher payouts. VC funds, while riskier, can offer outsized returns if portfolio companies succeed.
Long-Term Earnings Potential: VC vs. PE
When considering long-term earnings, both VC and PE offer significant potential, but the paths differ. Here’s an analysis:
- Carried Interest Over Time: In PE, carried interest can accumulate significantly over the life of a fund, leading to substantial long-term earnings. In VC, carried interest can be highly variable, with the potential for massive payouts if portfolio companies achieve successful exits.
- Risk and Reward: PE offers more stable, long-term earnings due to the lower risk associated with mature companies. VC, while riskier, can offer exponential returns if investments in startups pay off.
- Career Longevity: PE professionals often have longer, more stable careers with consistent earnings growth. VC professionals may experience more volatility but can achieve significant wealth if they back successful startups.
Does Morgan Stanley pay more than Goldman Sachs?
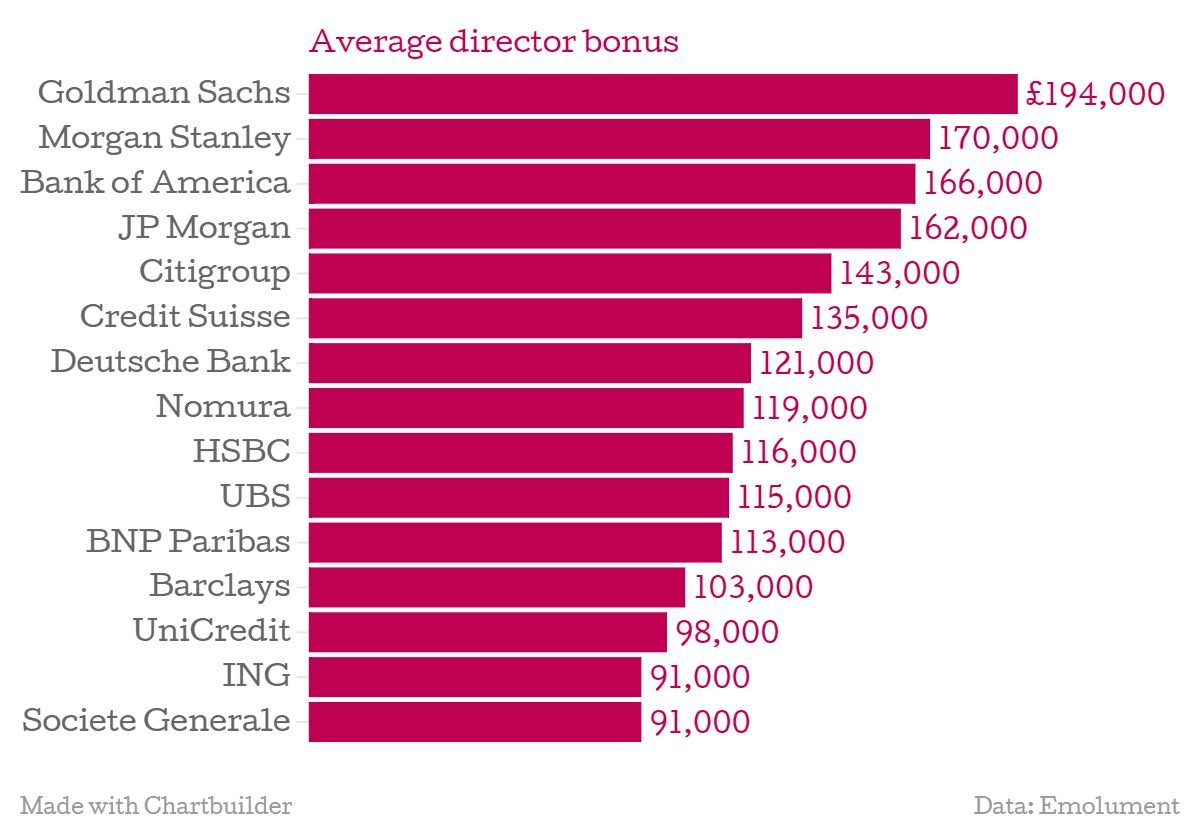
Does Morgan Stanley Pay More Than Goldman Sachs?
When comparing compensation between Morgan Stanley and Goldman Sachs, it depends on the role, level, and division. Historically, Goldman Sachs has been known for offering higher base salaries and bonuses, particularly in investment banking and trading roles. However, Morgan Stanley has been competitive in recent years, especially in wealth management and technology roles. Both firms adjust compensation based on market conditions and individual performance.
- Base Salaries: Goldman Sachs often offers higher base salaries for entry-level and mid-level positions.
- Bonuses: Goldman Sachs is traditionally known for more lucrative bonuses, especially in high-revenue divisions.
- Long-Term Incentives: Morgan Stanley may offer more long-term incentives like stock options or deferred compensation.
How Do Bonuses Compare Between Morgan Stanley and Goldman Sachs?
Bonuses are a significant part of compensation at both firms. Goldman Sachs is renowned for its generous bonus structure, particularly in investment banking and trading. Morgan Stanley, while competitive, tends to offer slightly lower bonuses but may balance this with other benefits like stock grants or deferred compensation.
- Investment Banking: Goldman Sachs typically leads in bonus payouts for investment bankers.
- Wealth Management: Morgan Stanley may offer more consistent bonuses in wealth management roles.
- Performance Metrics: Both firms tie bonuses to individual and company performance.
Which Firm Offers Better Compensation for Entry-Level Roles?
For entry-level roles, Goldman Sachs generally offers higher starting salaries and signing bonuses compared to Morgan Stanley. However, Morgan Stanley may provide more comprehensive training programs and career development opportunities, which can be valuable for long-term growth.
- Analyst Positions: Goldman Sachs analysts often earn more in base salary and bonuses.
- Training Programs: Morgan Stanley invests heavily in training and mentorship for new hires.
- Career Progression: Both firms offer clear pathways for advancement, but compensation growth may vary.
How Does Compensation Differ in Technology Roles?
In technology roles, Morgan Stanley has been increasingly competitive, often matching or exceeding Goldman Sachs in certain areas. Both firms recognize the importance of tech talent and offer competitive salaries, bonuses, and stock options to attract top candidates.
- Base Pay: Morgan Stanley may offer higher base salaries for specialized tech roles.
- Stock Options: Both firms provide stock-based compensation, but Morgan Stanley may offer more long-term incentives.
- Innovation Focus: Goldman Sachs emphasizes innovation, which can lead to higher bonuses for tech-driven projects.
What Are the Compensation Trends in Wealth Management?
In wealth management, Morgan Stanley often leads in compensation due to its strong focus on this division. While Goldman Sachs also offers competitive pay, Morgan Stanley's structure is more tailored to wealth management professionals, with a mix of base salary, bonuses, and long-term incentives.
- Client Revenue: Compensation is heavily tied to client assets and revenue generation.
- Long-Term Incentives: Morgan Stanley offers more deferred compensation and stock options in this division.
- Career Stability: Wealth management roles at Morgan Stanley may offer more consistent earnings over time.
Frequently Asked Questions from Our Community
What are the key differences between starting a career at Goldman Sachs versus Venture Capital?
Starting a career at Goldman Sachs typically involves working in a structured, hierarchical environment with well-defined roles, such as investment banking, sales, or trading. The firm offers extensive training programs, exposure to high-profile clients, and the opportunity to work on large-scale financial transactions. On the other hand, Venture Capital (VC) offers a more entrepreneurial and dynamic environment, where professionals often engage in sourcing deals, evaluating startups, and working closely with founders. While Goldman Sachs provides a broad financial foundation, VC focuses on early-stage investments and innovation, making it ideal for those interested in startups and emerging technologies.
Which career path offers better long-term growth opportunities: Goldman Sachs or Venture Capital?
Both Goldman Sachs and Venture Capital offer strong long-term growth opportunities, but they differ in nature. At Goldman Sachs, career progression is often linear, with clear milestones such as promotions to associate, vice president, and managing director. The firm’s global reputation and extensive network can open doors to senior roles in finance, corporate leadership, or even entrepreneurship. In contrast, Venture Capital provides a more varied trajectory, with opportunities to transition into roles like startup founder, angel investor, or partner at a VC firm. Success in VC often depends on building a strong track record of successful investments and cultivating a robust network within the startup ecosystem.
How does the work-life balance compare between Goldman Sachs and Venture Capital?
Work-life balance at Goldman Sachs is notoriously demanding, especially in roles like investment banking, where long hours and high-pressure deadlines are common. However, the firm offers competitive compensation and structured career paths, which can be rewarding for those willing to commit to the intensity. In Venture Capital, the work-life balance can vary significantly depending on the firm and stage of investments. Early-stage VCs may have more flexibility but often require frequent travel and networking. Later-stage VCs might involve fewer hours but higher stakes in decision-making. Ultimately, both paths require dedication, but VC may offer slightly more flexibility for those seeking a less rigid schedule.
Which career path is more suitable for someone interested in entrepreneurship: Goldman Sachs or Venture Capital?
For individuals passionate about entrepreneurship, Venture Capital is often the more suitable choice. VC professionals work closely with startups, gaining firsthand experience in evaluating business models, scaling companies, and understanding the challenges of entrepreneurship. This exposure can be invaluable for those looking to launch their own ventures in the future. While Goldman Sachs provides a strong foundation in finance and corporate strategy, its focus on large-scale transactions and established companies may not offer the same level of insight into the startup world. However, the skills and network gained at Goldman Sachs can still be beneficial for entrepreneurial endeavors, particularly in industries requiring significant capital or strategic partnerships.
Leave a Reply


Our Recommended Articles