Venture capital (VC) plays a pivotal role in fueling innovation and supporting startups with high-growth potential. However, navigating the complex world of venture capital can be challenging for entrepreneurs and investors alike. One question that often arises is whether there is a broker for venture capitalists—a professional or intermediary who facilitates connections between investors and startups. This article explores the concept of a VC broker, examining their role, the services they provide, and whether such intermediaries exist in the venture capital ecosystem. By understanding this dynamic, entrepreneurs and investors can better navigate the funding landscape and optimize their opportunities for success.
Is There a Broker for Venture Capitalists?
Venture capital (VC) is a specialized form of financing that involves investing in early-stage or high-growth companies with significant potential. While venture capitalists (VCs) typically source deals directly or through their networks, the concept of a broker for venture capitalists does exist, albeit in a less traditional sense. Unlike stockbrokers or real estate brokers, VC brokers act as intermediaries who connect startups seeking funding with venture capitalists looking for investment opportunities. These brokers often operate within niche markets or specific industries, providing tailored services to both parties.
What Does a Venture Capital Broker Do?
A venture capital broker serves as a middleman between startups and venture capitalists. Their primary role is to identify promising startups, evaluate their potential, and match them with suitable investors. They may also assist in structuring deals, negotiating terms, and ensuring that both parties' interests are aligned. Brokers often have extensive networks and industry expertise, making them valuable resources for startups and VCs alike.
See Also What is an Entrepreneur in Residence Eir What Do They Do How Does It Work
What is an Entrepreneur in Residence Eir What Do They Do How Does It WorkHow Do Venture Capital Brokers Operate?
Venture capital brokers operate by leveraging their industry connections and market knowledge. They typically charge a fee or commission for their services, which can be a percentage of the investment or a flat fee. Some brokers work independently, while others are part of larger firms specializing in venture capital matchmaking. Their operations often involve conducting due diligence, preparing pitch materials, and facilitating communication between startups and investors.
Benefits of Using a Venture Capital Broker
Using a venture capital broker offers several advantages. For startups, brokers provide access to a wider pool of investors and increase the likelihood of securing funding. For venture capitalists, brokers streamline the deal-sourcing process by presenting pre-vetted opportunities. Additionally, brokers can save time and reduce risks by ensuring that both parties are well-informed and aligned in their goals.
Challenges of Working with a Venture Capital Broker
Despite their benefits, working with a venture capital broker can present challenges. Brokers may charge high fees, which can be a burden for startups with limited resources. There is also the risk of misaligned incentives, as brokers may prioritize deals that offer higher commissions rather than those that are the best fit for the investor or startup. Additionally, not all brokers have the same level of expertise or credibility, making it essential to choose a reputable professional.
See Also Can I Make a Career in Venture Capital?
Can I Make a Career in Venture Capital?How to Choose the Right Venture Capital Broker
Selecting the right venture capital broker requires careful consideration. Startups and investors should evaluate a broker's track record, industry expertise, and network strength. It is also important to understand their fee structure and ensure transparency in their operations. Seeking recommendations and reading reviews can help in identifying a broker who aligns with your specific needs and goals.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Role | Middleman between startups and venture capitalists |
| Services | Deal sourcing, due diligence, negotiation, and matchmaking |
| Fees | Percentage of investment or flat fee |
| Benefits | Access to investors, streamlined processes, and expert guidance |
| Challenges | High fees, potential misalignment of incentives, and credibility concerns |

What is a venture capital broker?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Venturecapital-2f7ba3a27d0545f682a6238ea6b16cb9.png)
What is a Venture Capital Broker?
A venture capital broker is a professional or firm that acts as an intermediary between startups or early-stage companies seeking funding and venture capital firms or investors looking to invest in high-growth potential businesses. Their primary role is to facilitate the connection, negotiation, and deal-making process, ensuring that both parties achieve their objectives. Venture capital brokers often possess deep industry knowledge, a strong network of investors, and expertise in evaluating business models and financial projections.
See Also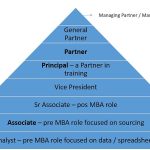 What Does It Mean to Be a Partner in a Venture Capital Firm?
What Does It Mean to Be a Partner in a Venture Capital Firm?Roles and Responsibilities of a Venture Capital Broker
The responsibilities of a venture capital broker are diverse and critical to the success of funding deals. These include:
- Identifying Investment Opportunities: They scout for startups or businesses with high growth potential that align with the interests of venture capital firms.
- Facilitating Negotiations: They act as mediators during discussions, ensuring that terms are fair and beneficial for both parties.
- Preparing Pitch Materials: They assist startups in creating compelling pitch decks and financial models to attract investors.
How Venture Capital Brokers Add Value to Startups
Venture capital brokers provide significant value to startups by:
- Access to Networks: They connect startups with a wide range of investors, including angel investors, venture capital firms, and private equity groups.
- Expert Guidance: They offer strategic advice on valuation, equity distribution, and negotiation tactics.
- Time Efficiency: They streamline the fundraising process, allowing entrepreneurs to focus on growing their business.
Key Skills Required for a Venture Capital Broker
To excel in this role, a venture capital broker must possess:
See Also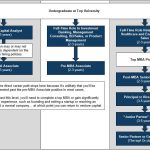 What is It Like to Be an Analyst at a Venture Capital Firm?
What is It Like to Be an Analyst at a Venture Capital Firm?- Financial Acumen: A deep understanding of financial modeling, valuation techniques, and investment analysis.
- Networking Abilities: Strong relationships with investors and a robust professional network.
- Negotiation Skills: The ability to mediate and secure favorable terms for both startups and investors.
Differences Between Venture Capital Brokers and Investment Bankers
While both roles involve facilitating financial transactions, there are key differences:
- Focus: Venture capital brokers specialize in early-stage and high-growth companies, whereas investment bankers often deal with larger, more established firms.
- Transaction Size: Venture capital brokers typically handle smaller deals compared to investment bankers, who manage large-scale mergers and acquisitions.
- Client Base: Venture capital brokers work closely with startups, while investment bankers cater to corporations and institutional clients.
How do I reach out to venture capitalists?

How to Identify the Right Venture Capitalists
To effectively reach out to venture capitalists, it is crucial to identify those who align with your industry, stage of business, and vision. Here’s how to do it:
See Also How Does One Become an Entrepreneur in Residence at a Venture Capital Firm
How Does One Become an Entrepreneur in Residence at a Venture Capital Firm- Research their portfolio: Look for venture capitalists who have invested in companies similar to yours in terms of industry, size, and growth stage.
- Understand their investment thesis: Review their public statements, blogs, or interviews to understand their focus areas and criteria for investments.
- Check their track record: Analyze their past investments to see if they have a history of supporting startups through to successful exits.
How to Prepare Before Contacting Venture Capitalists
Preparation is key to making a strong impression when reaching out to venture capitalists. Follow these steps:
- Refine your pitch deck: Ensure your pitch deck is concise, visually appealing, and clearly communicates your business model, market opportunity, and growth strategy.
- Prepare financial projections: Have detailed and realistic financial projections ready to demonstrate your business’s potential.
- Know your metrics: Be ready to discuss key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value (LTV), and monthly recurring revenue (MRR).
How to Craft a Compelling Outreach Message
Your initial message to a venture capitalist should be concise, personalized, and compelling. Here’s how to structure it:
- Start with a strong subject line: Use a subject line that grabs attention, such as “Revolutionizing [Industry] with [Your Unique Solution].”
- Personalize the introduction: Mention why you’re reaching out to them specifically, referencing their past investments or expertise.
- Highlight key points: Briefly outline your business, traction, and what you’re seeking in terms of funding and partnership.
How to Leverage Warm Introductions
Warm introductions can significantly increase your chances of getting a response from venture capitalists. Here’s how to secure one:
- Tap into your network: Ask mentors, advisors, or other founders if they can introduce you to venture capitalists they know.
- Use LinkedIn strategically: Identify mutual connections and request introductions through them.
- Attend industry events: Networking at conferences or meetups can help you build relationships that lead to introductions.
How to Follow Up Effectively
Following up is essential if you don’t receive an immediate response. Here’s how to do it professionally:
- Wait for the right time: Give the venture capitalist at least a week before sending a follow-up email.
- Add value in your follow-up: Share updates on your business, such as new milestones, partnerships, or product launches.
- Be persistent but polite: Avoid being pushy, but don’t hesitate to follow up a few times if necessary.
How much money do I need to start a VC firm?

Initial Capital Requirements for a VC Firm
Starting a venture capital (VC) firm requires a significant amount of capital, as the primary function of a VC firm is to invest in startups and early-stage companies. The amount of money needed depends on the scale and scope of the firm. Here are the key considerations:
- Fund Size: A typical VC fund ranges from $10 million to $100 million or more. The larger the fund, the more startups you can invest in and the greater your potential returns.
- Operational Costs: You will need to cover salaries, office space, legal fees, and other administrative expenses. These costs can range from $500,000 to $2 million annually.
- Reserve Capital: It’s essential to set aside additional capital for follow-on investments in portfolio companies, as startups often require multiple funding rounds.
Legal and Regulatory Costs
Establishing a VC firm involves navigating complex legal and regulatory requirements. These costs can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the structure of the firm. Key expenses include:
- Legal Fees: Drafting partnership agreements, fund formation documents, and compliance with securities laws can cost between $50,000 and $200,000.
- Registration Fees: Registering with regulatory bodies like the SEC in the U.S. or equivalent agencies in other countries may incur additional costs.
- Ongoing Compliance: Maintaining compliance with regulations requires ongoing legal and accounting support, which can add to your annual expenses.
Building a Team and Infrastructure
A successful VC firm requires a skilled team and robust infrastructure to identify, evaluate, and manage investments. Consider the following:
- Hiring Talent: You’ll need experienced investment professionals, analysts, and support staff. Salaries for top talent can range from $100,000 to $500,000 annually.
- Office Space: Depending on your location, office rent and utilities can cost between $50,000 and $200,000 per year.
- Technology and Tools: Investing in software for deal flow management, financial analysis, and communication tools is essential and can cost $10,000 to $50,000 annually.
Fundraising and Investor Relations
Raising capital for your VC fund is a critical step and involves significant effort and resources. Key aspects include:
- Marketing Materials: Creating pitch decks, fund prospectuses, and other materials to attract investors can cost $10,000 to $50,000.
- Networking Events: Attending industry conferences and events to build relationships with potential investors can cost $5,000 to $20,000 annually.
- Investor Reporting: Providing regular updates and financial reports to your limited partners (LPs) requires time and resources, including accounting and administrative support.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Managing risks and preparing for unforeseen challenges is crucial for the long-term success of a VC firm. Consider the following:
- Diversification: Allocating funds across multiple startups and industries reduces the risk of significant losses.
- Reserve Funds: Setting aside 10-20% of your total fund for unexpected expenses or follow-on investments is a common practice.
- Insurance: Obtaining professional liability insurance and other coverage can protect your firm from legal and financial risks.
How much do VC advisors get paid?
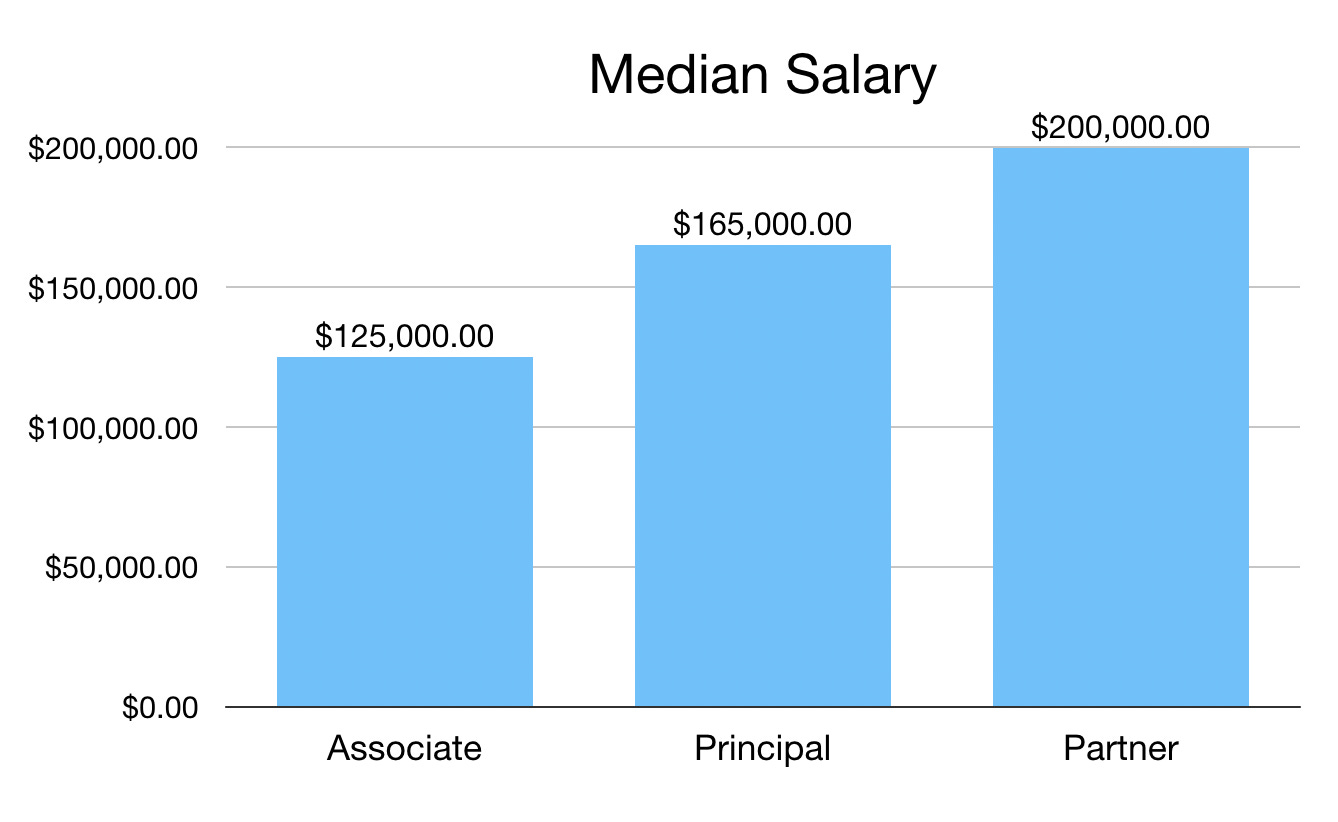
How Much Do VC Advisors Typically Earn?
Venture Capital (VC) advisors are compensated based on their experience, the stage of the startups they advise, and the value they bring to the table. Their earnings can vary widely, but they generally fall into the following categories:
- Cash Compensation: Advisors may receive a fixed fee, often ranging from $1,000 to $10,000 per month, depending on the startup's funding stage and the advisor's expertise.
- Equity Stake: Many advisors are granted equity, typically between 0.25% and 1% of the company's shares, which can become highly valuable if the startup succeeds.
- Hybrid Models: Some advisors combine cash and equity, ensuring immediate income while retaining a stake in the company's future growth.
Factors Influencing VC Advisor Compensation
The amount a VC advisor earns depends on several key factors, including their role, the startup's stage, and the industry. Below are the most influential factors:
- Experience and Reputation: Seasoned advisors with a proven track record command higher fees and larger equity stakes.
- Startup Stage: Early-stage startups often offer more equity but less cash, while later-stage companies may provide higher cash compensation.
- Industry: Advisors in high-growth sectors like tech or biotech may earn more due to the higher potential returns.
Cash vs. Equity: Which is More Common?
VC advisors often face the choice between cash and equity, and the decision depends on the startup's financial situation and the advisor's risk tolerance. Here’s a breakdown:
- Cash Payments: More common in later-stage startups with sufficient funding to pay advisors upfront.
- Equity Grants: Preferred by early-stage startups that lack cash but want to incentivize advisors with potential future rewards.
- Balanced Approach: Many advisors negotiate a mix of both to mitigate risk while retaining upside potential.
How Do VC Advisors Negotiate Their Fees?
Negotiating compensation as a VC advisor requires a clear understanding of the startup's needs and the advisor's value. Key strategies include:
- Assessing the Startup's Budget: Understanding the company's financial health helps in determining realistic compensation.
- Highlighting Expertise: Advisors with niche skills or industry connections can leverage these to negotiate higher fees or equity.
- Setting Clear Expectations: Defining the scope of work and deliverables ensures both parties agree on the advisor's role and compensation.
What Are the Risks and Rewards for VC Advisors?
Becoming a VC advisor comes with both risks and rewards, depending on the startup's success and the compensation structure. Here’s what to consider:
- High Rewards: Equity stakes can yield significant returns if the startup is acquired or goes public.
- Financial Risk: Early-stage startups have a high failure rate, making equity compensation potentially worthless.
- Reputation Risk: Associating with a failed startup can impact an advisor's professional standing, while success can enhance their reputation.
Frequently Asked Questions from Our Community
What is a venture capital broker?
A venture capital broker is a professional or firm that acts as an intermediary between venture capitalists and businesses seeking funding. These brokers help startups and growing companies connect with investors who are willing to provide capital in exchange for equity. They often have extensive networks and expertise in matching the right investors with the right opportunities, ensuring that both parties benefit from the deal.
How does a venture capital broker work?
A venture capital broker typically begins by understanding the needs and goals of the business seeking funding. They then identify potential venture capitalists or investment firms that align with the business's industry, stage, and growth potential. The broker facilitates introductions, assists in preparing pitch materials, and may even negotiate terms on behalf of the business. Their role is to streamline the process and increase the chances of securing funding.
Why should I use a venture capital broker?
Using a venture capital broker can save time and increase the likelihood of securing funding. Brokers have access to a wide network of venture capitalists and understand the intricacies of the investment process. They can help businesses present their case effectively, avoid common pitfalls, and negotiate favorable terms. For startups and small businesses, a broker can be a valuable partner in navigating the competitive world of venture capital.
Are there fees associated with hiring a venture capital broker?
Yes, most venture capital brokers charge fees for their services. These fees can vary depending on the broker and the complexity of the deal. Some brokers may charge a success fee, which is a percentage of the funding secured, while others may charge upfront or retainer fees. It's important to discuss and agree on the fee structure before engaging a broker to ensure transparency and avoid surprises later in the process.
Leave a Reply


Our Recommended Articles