Preparing for a venture capital (VC) interview, particularly when it involves financial modeling, requires a solid understanding of both the technical and strategic aspects of the role. Venture capital firms seek candidates who can analyze investment opportunities, assess risks, and project financial outcomes with precision. This article outlines the key elements you should master, including building robust financial models, understanding valuation techniques, and interpreting key metrics like burn rate, runway, and cap tables. Additionally, it covers the importance of aligning your modeling approach with the firm’s investment philosophy and how to effectively communicate your insights during the interview process.
- What You Need to Know About Modeling for a Venture Capital Interview
- What is a venture capital interview like?
- How to nail a VC interview?
- How to prepare for a venture capital job?
- What models are used in venture capital?
- Frequently Asked Questions from Our Community
- What are the key components of financial modeling for a venture capital interview?
- How should I approach building a startup valuation model?
- What are the most common mistakes to avoid in venture capital modeling?
- How can I demonstrate my understanding of venture capital metrics during the interview?
What You Need to Know About Modeling for a Venture Capital Interview
Understanding the Basics of Financial Modeling
Financial modeling is a critical skill in venture capital. It involves creating a mathematical representation of a company's financial performance. This model helps in forecasting future revenues, expenses, and cash flows. For a venture capital interview, you should be familiar with the key components of a financial model, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Additionally, understanding how to project growth rates, calculate valuation multiples, and perform sensitivity analysis is essential.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Income Statement | Shows the company's revenues, expenses, and profits over a period. |
| Balance Sheet | Provides a snapshot of the company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. |
| Cash Flow Statement | Details the cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing, and financing activities. |
Key Metrics to Focus On
In venture capital, certain metrics are more important than others. These include Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Lifetime Value (LTV), Burn Rate, and Runway. Understanding these metrics and how they interrelate is crucial for assessing the health and potential of a startup. For instance, a low CAC relative to LTV indicates a sustainable business model, while a high burn rate with a short runway may signal financial distress.
See Also Why Should I Choose Equity Crowdfunding Instead of Venture Capital
Why Should I Choose Equity Crowdfunding Instead of Venture Capital| Metric | Importance |
|---|---|
| CAC | Measures the cost to acquire a new customer. |
| LTV | Estimates the total revenue a company can expect from a single customer. |
| Burn Rate | Indicates how quickly a company is spending its cash reserves. |
| Runway | Shows how long the company can operate before needing additional funding. |
Valuation Techniques
Valuation is a cornerstone of venture capital. You should be familiar with various valuation methods, such as Discounted Cash Flow (DCF), Comparable Company Analysis, and Precedent Transactions. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and understanding when to apply each is key. For example, DCF is useful for companies with predictable cash flows, while Comparable Company Analysis is more applicable for startups in well-established industries.
| Method | Use Case |
|---|---|
| DCF | Best for companies with stable and predictable cash flows. |
| Comparable Company Analysis | Useful for startups in industries with many public comparables. |
| Precedent Transactions | Ideal for understanding what similar companies have been acquired for. |
Sensitivity and Scenario Analysis
Sensitivity and scenario analysis are vital tools in financial modeling. They help assess how changes in key assumptions impact the model's outcomes. For instance, you might analyze how a 10% increase in customer churn rate affects the company's revenue. This type of analysis is crucial for understanding the range of possible outcomes and preparing for different scenarios.
| Analysis Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity Analysis | Examines the impact of changing one variable at a time. |
| Scenario Analysis | Evaluates the effect of multiple variables changing simultaneously. |
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
When building financial models, there are several common pitfalls to avoid. These include overcomplicating the model, using unrealistic assumptions, and failing to validate the model with real-world data. It's also important to ensure that the model is flexible and can be easily updated as new information becomes available. Avoiding these mistakes will help you create a more accurate and reliable financial model.
See Also Which Venture Capital Firms Have Major Offices in Chicago?
Which Venture Capital Firms Have Major Offices in Chicago?| Pitfall | Solution |
|---|---|
| Overcomplicating the Model | Keep the model as simple as possible while still capturing the necessary details. |
| Unrealistic Assumptions | Base assumptions on historical data and industry benchmarks. |
| Lack of Validation | Regularly compare model outputs with actual results to ensure accuracy. |

What is a venture capital interview like?

Understanding the Structure of a Venture Capital Interview
A venture capital interview typically involves multiple stages designed to assess both your technical skills and cultural fit within the firm. The process often includes:
- Initial Screening: A phone or video call to evaluate your background and interest in venture capital.
- Case Study: You may be asked to analyze a startup or market opportunity to demonstrate your analytical and strategic thinking.
- Technical Questions: These focus on your understanding of financial modeling, valuation, and market analysis.
- Behavioral Questions: These assess your teamwork, decision-making, and problem-solving abilities.
- Final Round: Often involves meeting with senior partners to discuss your fit with the firm’s long-term goals.
Key Skills Evaluated in a Venture Capital Interview
Venture capital firms look for candidates with a unique blend of skills. The following are often evaluated:
See Also How to Start a Tech Company with no Experience
How to Start a Tech Company with no Experience- Analytical Abilities: Your capacity to assess market trends, financial statements, and business models.
- Networking Skills: Your ability to build relationships with entrepreneurs and other investors.
- Strategic Thinking: How well you can identify high-potential startups and growth opportunities.
- Communication: Your ability to articulate complex ideas clearly and persuasively.
- Passion for Startups: Genuine interest in innovation and entrepreneurship.
Common Questions Asked in a Venture Capital Interview
During a venture capital interview, you can expect a mix of technical and behavioral questions. Some common ones include:
- Walk me through an investment thesis you would pursue. This tests your strategic thinking and market knowledge.
- How would you value a startup? This assesses your understanding of valuation methodologies like DCF or comparables.
- Tell me about a time you worked in a team. This evaluates your teamwork and collaboration skills.
- What industries are you most excited about? This gauges your passion and industry knowledge.
- How do you handle failure? This tests your resilience and learning mindset.
Preparing for a Venture Capital Interview
Preparation is crucial for succeeding in a venture capital interview. Here’s how you can prepare effectively:
- Research the Firm: Understand their portfolio, investment focus, and recent deals.
- Practice Case Studies: Familiarize yourself with analyzing startups and market opportunities.
- Brush Up on Financial Concepts: Review valuation methods, financial modeling, and key metrics like CAC and LTV.
- Prepare Your Story: Be ready to discuss your background, achievements, and why you’re interested in venture capital.
- Network: Speak with current or former employees to gain insights into the firm’s culture and expectations.
What to Expect During the Final Round
The final round of a venture capital interview is often the most rigorous. Here’s what to expect:
- Partner Meetings: You’ll meet with senior partners who will assess your fit with the firm’s vision and culture.
- Deep Dive Discussions: Be prepared for in-depth conversations about your investment philosophy and market insights.
- Scenario-Based Questions: You may be asked to solve real-world problems or evaluate hypothetical investment opportunities.
- Cultural Fit Assessment: The firm will evaluate how well you align with their values and working style.
- Decision Timeline: Firms often provide a clear timeline for when you can expect feedback or an offer.
How to nail a VC interview?
1. Research the VC Firm and Its Portfolio
Before stepping into a VC interview, it is crucial to thoroughly research the VC firm and its portfolio companies. This demonstrates your genuine interest and helps you tailor your pitch to align with their investment philosophy.
- Understand the firm’s investment thesis and focus areas (e.g., early-stage, SaaS, healthcare).
- Analyze their portfolio to identify patterns in the types of startups they back.
- Be prepared to discuss how your startup fits into their existing portfolio.
2. Master Your Pitch
A compelling and concise pitch is essential to capture the attention of venture capitalists. Your pitch should clearly articulate your value proposition, market opportunity, and growth potential.
- Start with a strong problem statement that resonates with the VC.
- Highlight your unique solution and how it stands out from competitors.
- Include key metrics, such as traction, revenue, or user growth, to back your claims.
3. Anticipate Tough Questions
VCs are known for asking challenging questions to test your knowledge and resilience. Being prepared for these questions can set you apart from other candidates.
- Practice answering questions about your business model and scalability.
- Be ready to defend your market assumptions and competitive landscape.
- Have a clear plan for how you will use the funding to achieve milestones.
4. Showcase Your Team’s Strengths
Venture capitalists invest in teams as much as they invest in ideas. Highlighting the strengths and expertise of your team can build confidence in your ability to execute.
- Emphasize the relevant experience of your co-founders and key team members.
- Discuss how your team’s skills complement each other and address the challenges ahead.
- Share examples of past successes or projects that demonstrate your team’s capabilities.
5. Demonstrate Traction and Momentum
VCs want to see evidence that your startup is gaining traction and has the potential for rapid growth. Providing concrete data can significantly strengthen your case.
- Present metrics such as customer acquisition, retention rates, or revenue growth.
- Highlight any partnerships, pilot programs, or notable achievements.
- Show a clear roadmap for future growth and how the investment will accelerate it.
How to prepare for a venture capital job?

Understanding the Venture Capital Industry
To prepare for a venture capital job, it is essential to understand the industry thoroughly. Venture capital (VC) involves investing in early-stage or high-growth companies with significant potential. To build a strong foundation:
- Research the VC ecosystem: Learn about key players, investment stages (seed, Series A, B, etc.), and how VCs generate returns.
- Follow industry trends: Stay updated on emerging technologies, market shifts, and successful startups.
- Study successful VC firms: Analyze their investment strategies, portfolio companies, and decision-making processes.
Building Financial and Analytical Skills
Venture capital roles require strong financial and analytical skills. These skills are critical for evaluating startups and making investment decisions. Focus on:
- Mastering financial modeling: Learn to create and interpret financial statements, cash flow projections, and valuation models.
- Understanding key metrics: Familiarize yourself with metrics like burn rate, customer acquisition cost (CAC), and lifetime value (LTV).
- Developing data analysis skills: Use tools like Excel, SQL, or Python to analyze market data and startup performance.
Gaining Relevant Experience
Practical experience is invaluable for breaking into venture capital. Consider the following steps:
- Work in startups: Gain firsthand experience in a startup environment to understand their challenges and growth strategies.
- Pursue internships in VC firms: Apply for internships or analyst roles to learn directly from industry professionals.
- Network with founders and investors: Attend industry events, join startup communities, and build relationships with key stakeholders.
Developing a Strong Network
Networking is a cornerstone of venture capital. Building a robust professional network can open doors to opportunities. Focus on:
- Attending industry events: Participate in conferences, pitch nights, and networking sessions to meet investors and entrepreneurs.
- Leveraging LinkedIn: Connect with VC professionals, share insights, and engage in discussions to build your presence.
- Joining VC communities: Become a member of organizations like the National Venture Capital Association (NVCA) or local angel investor groups.
Enhancing Communication and Presentation Skills
Effective communication is crucial in venture capital, as you’ll need to present investment opportunities and negotiate deals. To improve:
- Practice pitching: Learn to articulate investment theses clearly and concisely.
- Develop storytelling skills: Use narratives to explain complex ideas and make compelling cases for investments.
- Hone negotiation techniques: Understand how to structure deals, negotiate terms, and build win-win agreements.
What models are used in venture capital?
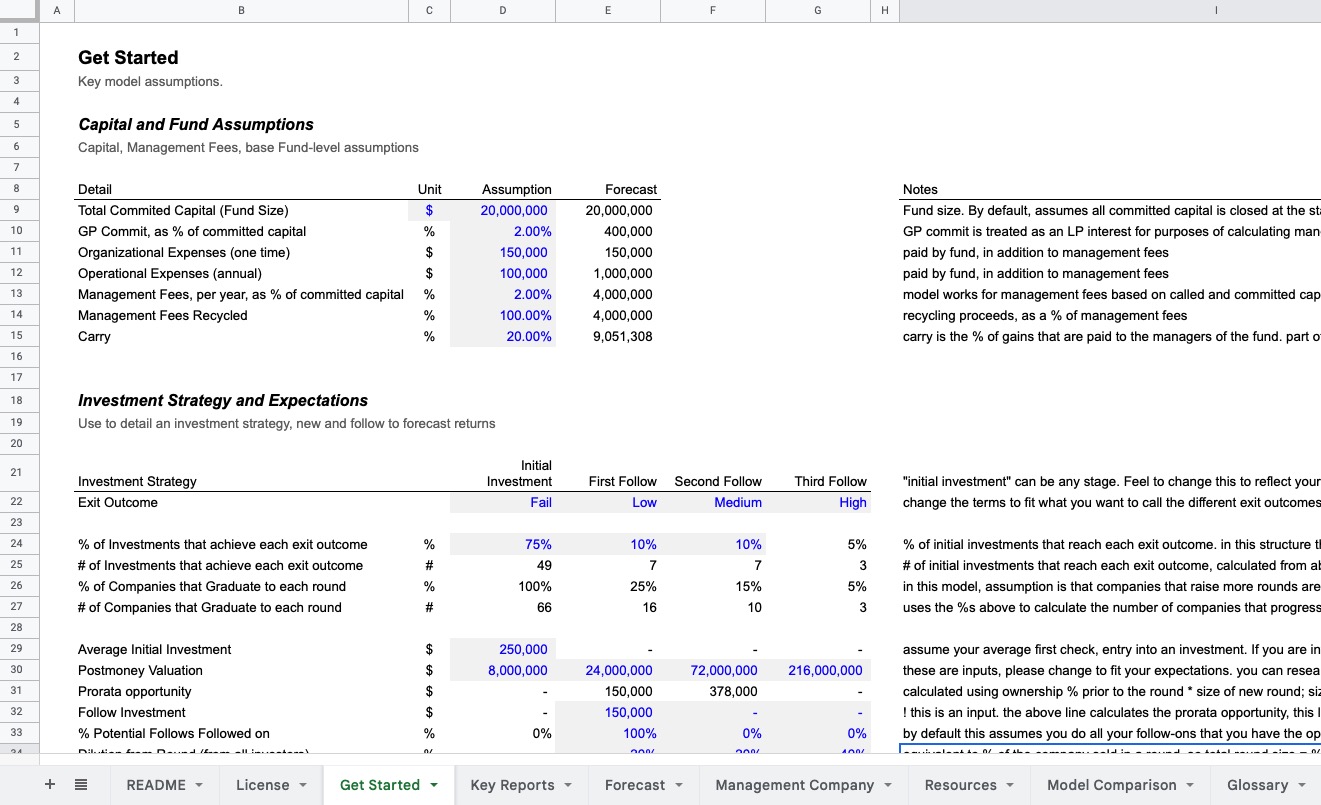
1. The Venture Capital Investment Model
The venture capital investment model is the primary framework used by venture capitalists to identify, evaluate, and invest in high-potential startups. This model involves several key steps:
- Deal Sourcing: Identifying potential investment opportunities through networks, referrals, or pitch events.
- Due Diligence: Conducting thorough research on the startup's market, team, product, and financials.
- Valuation: Determining the startup's worth using methods like discounted cash flow or comparable company analysis.
- Term Sheet Negotiation: Outlining the terms of the investment, including equity stakes and investor rights.
- Post-Investment Management: Providing ongoing support and guidance to the startup to ensure growth and success.
2. The Portfolio Diversification Model
The portfolio diversification model is a strategy used by venture capitalists to spread risk across multiple investments. This approach ensures that the potential failure of one startup does not significantly impact the overall portfolio. Key aspects include:
- Sector Allocation: Investing in startups across various industries to mitigate sector-specific risks.
- Stage Diversification: Balancing investments between early-stage, growth-stage, and late-stage startups.
- Geographic Spread: Allocating funds to startups in different regions or countries to reduce location-based risks.
- Investment Size: Varying the amount invested in each startup to manage exposure.
- Exit Strategy: Planning for diverse exit options such as IPOs, acquisitions, or secondary sales.
3. The Value-Added Model
The value-added model focuses on providing more than just capital to startups. Venture capitalists using this model actively contribute to the growth and success of their portfolio companies. Key components include:
- Mentorship: Offering guidance and advice to founders on strategy, operations, and scaling.
- Network Access: Connecting startups with industry experts, potential partners, and customers.
- Operational Support: Assisting with hiring, marketing, and other operational challenges.
- Strategic Planning: Helping startups refine their business models and long-term goals.
- Follow-On Funding: Providing additional capital in subsequent funding rounds to support growth.
The syndication model involves multiple venture capital firms co-investing in a startup. This approach allows for shared risk and increased capital availability. Key features include:
- Lead Investor: One firm takes the lead in negotiating terms and coordinating the investment.
- Co-Investors: Other firms join the investment round, contributing additional funds.
- Risk Sharing: The financial risk is distributed among all participating investors.
- Resource Pooling: Combining expertise and networks from multiple firms to benefit the startup.
- Exit Coordination: Collaborating on exit strategies to maximize returns for all investors.
5. The Stage-Specific Model
The stage-specific model tailors investment strategies to the developmental stage of the startup. This model recognizes that different stages require different approaches. Key stages include:
- Seed Stage: Providing initial funding to validate the business idea and develop a prototype.
- Early Stage: Supporting startups in building their team, product, and market presence.
- Growth Stage: Investing in scaling operations, expanding markets, and increasing revenue.
- Late Stage: Preparing startups for exit through IPOs or acquisitions.
- Bridge Financing: Offering short-term funding to bridge gaps between major funding rounds.
Frequently Asked Questions from Our Community
What are the key components of financial modeling for a venture capital interview?
Financial modeling for a venture capital interview typically involves understanding and building models that evaluate a company's financial performance and potential. Key components include revenue projections, expense forecasts, cash flow analysis, and valuation metrics such as discounted cash flow (DCF) and comparable company analysis. You should also be familiar with cap tables to understand equity distribution and dilution. Additionally, knowing how to model scenarios (best-case, base-case, and worst-case) is crucial to demonstrate your ability to assess risk and opportunity.
How should I approach building a startup valuation model?
When building a startup valuation model, start by gathering data on the company's historical financials, market size, and growth potential. Use revenue multiples or DCF analysis to estimate the company's value. Be prepared to justify your assumptions, such as growth rates and discount rates, as venture capitalists will scrutinize these. Additionally, consider incorporating sensitivity analysis to show how changes in key variables impact the valuation. Understanding the stage of the startup (seed, Series A, etc.) is also critical, as earlier-stage companies often rely more on qualitative factors.
What are the most common mistakes to avoid in venture capital modeling?
Common mistakes in venture capital modeling include overestimating revenue growth, underestimating operating expenses, and failing to account for cash burn rates. Another frequent error is neglecting to include dilution effects in the cap table, which can significantly impact equity stakes. Additionally, avoid using overly complex models that lack clarity; simplicity and transparency are key. Lastly, ensure your assumptions are realistic and backed by data, as overly optimistic projections can undermine your credibility.
How can I demonstrate my understanding of venture capital metrics during the interview?
To demonstrate your understanding of venture capital metrics, be prepared to discuss key terms such as Internal Rate of Return (IRR), Cash-on-Cash Return, and Valuation Cap. Explain how these metrics are used to evaluate investment opportunities and assess risk. You should also be able to interpret financial statements and calculate metrics like LTV/CAC ratio (Lifetime Value to Customer Acquisition Cost) and gross margins. Providing examples of how you've applied these metrics in past experiences or case studies will further showcase your expertise.
Leave a Reply



Our Recommended Articles