Accepting venture capital (VC) can be a game-changer for startups, providing the financial resources needed to scale operations, innovate, and compete in the market. However, this funding avenue comes with significant trade-offs. One major drawback is the loss of control and autonomy that founders often experience. Venture capitalists typically demand equity in exchange for their investment, which can lead to diluted ownership and decision-making power. Additionally, VC investors may push for aggressive growth strategies or prioritize short-term gains over long-term vision, potentially misaligning with the founder's original goals. Understanding these implications is crucial for entrepreneurs weighing the pros and cons of venture capital.
- What is a Major Drawback of Accepting Venture Capital?
- What is a drawback of using venture capital?
- Which of the following is a disadvantage of venture capital?
- What is the biggest risk in venture capital?
- What are venture capital advantages and disadvantages?
- Frequently Asked Questions from Our Community
What is a Major Drawback of Accepting Venture Capital?
Accepting venture capital can be a double-edged sword for startups and growing businesses. While it provides the necessary funds to scale operations, it often comes with significant trade-offs. One of the major drawbacks is the loss of control and autonomy over the company. Venture capitalists typically require equity in exchange for their investment, which means they gain a say in key business decisions. This can lead to conflicts, especially if the founders and investors have differing visions for the company's future.
1. Loss of Decision-Making Power
When you accept venture capital, you often give up a portion of your company's equity. This means that investors gain a seat at the table when it comes to making critical decisions. Founders may find themselves overruled on matters like hiring, product development, or even exit strategies. This loss of control can be frustrating and may lead to a misalignment of goals between the founders and the investors.
See Also What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Venture Capital as a Source of Financing Business
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Venture Capital as a Source of Financing Business2. Pressure to Deliver Rapid Growth
Venture capitalists invest with the expectation of high returns within a relatively short timeframe. This creates immense pressure on the company to achieve rapid growth. Startups may be forced to prioritize short-term gains over long-term sustainability, potentially compromising their core values or mission. This pressure can also lead to burnout among team members.
3. Dilution of Ownership
Accepting venture capital often results in the dilution of ownership. As more investors come on board, the founders' share of the company decreases. Over time, this can reduce the founders' financial stake and influence in the business. In some cases, founders may even end up with a minority stake in the company they started.
4. Risk of Losing the Company
If a startup fails to meet the performance expectations set by its investors, the venture capitalists may take drastic measures. This could include replacing the founders with new management or even selling the company to recoup their investment. Such actions can result in the founders losing their vision and control over the business they built.
See Also What Are All Pros and Cons of Venture Capital?
What Are All Pros and Cons of Venture Capital?5. Limited Flexibility in Exit Strategies
Venture capitalists often have specific exit strategies in mind, such as an IPO or acquisition, to maximize their returns. This can limit the founders' flexibility in choosing how and when to exit the business. Founders may be forced to pursue an exit that aligns with the investors' interests rather than their own.
| Drawback | Impact |
|---|---|
| Loss of Decision-Making Power | Founders may lose control over key business decisions. |
| Pressure to Deliver Rapid Growth | Short-term growth may be prioritized over long-term sustainability. |
| Dilution of Ownership | Founders' equity stake decreases as more investors join. |
| Risk of Losing the Company | Founders may be replaced or the company sold if expectations aren't met. |
| Limited Flexibility in Exit Strategies | Founders may have to align with investors' preferred exit plans. |

What is a drawback of using venture capital?

Loss of Control and Decision-Making Power
One of the primary drawbacks of using venture capital is the potential loss of control over your business. Venture capitalists often require a significant equity stake in exchange for their investment, which can lead to:
See Also What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Each of the Top Venture Capital Firms for Founders
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Each of the Top Venture Capital Firms for Founders- Reduced autonomy in making key business decisions.
- Pressure to align with the investor's vision rather than your own.
- Potential conflicts over the strategic direction of the company.
Dilution of Ownership
When you accept venture capital, you typically give up a portion of your company's equity. This can result in:
- Reduced ownership percentage for the original founders.
- Less financial benefit from future profits or exits.
- Potential challenges in raising additional funding without further dilution.
Pressure for Rapid Growth
Venture capitalists often expect a high return on their investment, which can lead to:
- Unrealistic growth targets that may strain the company.
- Focus on short-term gains over long-term sustainability.
- Increased risk of burnout for the founding team.
Potential for Misaligned Interests
Venture capitalists and founders may not always have the same goals, which can result in:
See Also What Are the Legal Requirements to Start a Woodworking Business in the Us?
What Are the Legal Requirements to Start a Woodworking Business in the Us?- Conflicts over exit strategies, such as selling the company versus long-term growth.
- Disagreements on how to allocate resources or prioritize projects.
- Pressure to prioritize investor returns over other stakeholders, such as employees or customers.
High Expectations and Accountability
Venture capitalists often demand regular updates and measurable progress, which can lead to:
- Increased scrutiny on performance metrics and milestones.
- Pressure to meet aggressive timelines, even if they are not realistic.
- Potential strain on the company's culture and team dynamics.
Which of the following is a disadvantage of venture capital?
High Cost of Capital
One of the primary disadvantages of venture capital is the high cost of capital. Venture capitalists typically expect a significant return on their investment, often in the form of equity or a share of the company's profits. This can lead to:
- Dilution of ownership: Founders may lose a substantial portion of their equity, reducing their control over the company.
- Pressure for rapid growth: Venture capitalists often push for quick returns, which can lead to unsustainable business practices.
- Higher financial burden: The cost of servicing the investment can be substantial, especially if the company does not achieve the expected growth.
Loss of Control
Another significant disadvantage is the potential loss of control over the company. When venture capitalists invest, they often require a say in the company's operations and strategic decisions. This can result in:
- Interference in management: Venture capitalists may impose their own management team or influence key decisions.
- Conflict of interest: The goals of the venture capitalists may not always align with those of the founders, leading to disagreements.
- Reduced autonomy: Founders may find themselves unable to make decisions without the approval of their investors.
Short-Term Focus
Venture capital often comes with a short-term focus, which can be detrimental to the long-term health of the company. This focus can lead to:
- Neglect of long-term strategy: The pressure to deliver quick results can cause the company to overlook important long-term goals.
- Overemphasis on growth: Companies may prioritize rapid expansion over sustainable development, risking burnout or failure.
- Misalignment with company vision: The short-term objectives of the investors may conflict with the original vision of the founders.
Risk of Failure
Venture capital investments are inherently risky, and the risk of failure is a significant disadvantage. This risk can manifest in several ways:
- High failure rate: Many startups fail to achieve the expected growth, leading to a loss of investment.
- Financial instability: The reliance on venture capital can create financial instability if the company does not meet its targets.
- Reputation damage: Failure can harm the reputation of both the company and its founders, making it harder to secure future funding.
Limited Exit Options
Finally, venture capital can limit the exit options available to the founders. This limitation can be problematic in several ways:
- Pressure to sell: Venture capitalists may push for an early exit, such as a sale or IPO, which may not align with the founders' plans.
- Reduced flexibility: The terms of the investment may restrict the founders' ability to explore other exit strategies.
- Potential for undervaluation: In a forced exit, the company may be sold for less than its potential value, resulting in a loss for the founders.
What is the biggest risk in venture capital?

Market Risk
Market risk is one of the most significant challenges in venture capital. It refers to the possibility that the market for a startup's product or service may not develop as anticipated. This can occur due to changes in consumer preferences, economic downturns, or the emergence of superior competing technologies. To mitigate market risk, venture capitalists often:
- Conduct thorough market research to understand demand and competition.
- Diversify their investment portfolio across various industries and stages.
- Monitor market trends and adjust strategies accordingly.
Execution Risk
Execution risk involves the potential that a startup may fail to implement its business plan effectively. This can stem from poor management, operational inefficiencies, or inadequate resources. Key strategies to address execution risk include:
- Investing in experienced management teams with a proven track record.
- Providing mentorship and operational support to portfolio companies.
- Setting clear milestones and regularly reviewing progress.
Technology Risk
Technology risk pertains to the possibility that a startup's technology may not perform as expected or may become obsolete. This is particularly relevant in fast-evolving sectors like biotechnology and software. To manage technology risk, venture capitalists often:
- Assess the scalability and robustness of the technology.
- Invest in R&D to stay ahead of technological advancements.
- Engage technical experts to evaluate the technology's potential.
Regulatory Risk
Regulatory risk involves the potential for changes in laws or regulations that could adversely affect a startup's operations. This is especially critical in industries like healthcare, finance, and energy. Strategies to mitigate regulatory risk include:
- Staying informed about regulatory changes and their potential impacts.
- Engaging legal experts to ensure compliance with current laws.
- Advocating for favorable policies through industry associations.
Financial Risk
Financial risk refers to the possibility that a startup may run out of capital before achieving profitability. This can result from poor financial management, unexpected expenses, or difficulties in securing additional funding. To address financial risk, venture capitalists typically:
- Conduct detailed financial due diligence before investing.
- Provide staged funding based on achieving specific milestones.
- Maintain a reserve fund to support portfolio companies in need.
What are venture capital advantages and disadvantages?
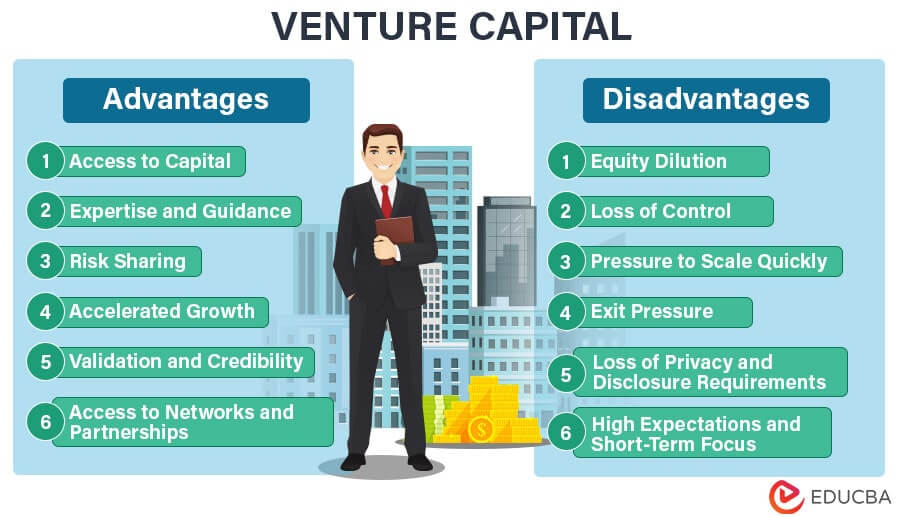
Advantages of Venture Capital
Venture capital offers several benefits for startups and growing businesses. Here are the key advantages:
- Access to Capital: Venture capital provides significant funding that can help startups scale quickly, which might not be possible through traditional financing methods.
- Expertise and Mentorship: Venture capitalists often bring valuable industry experience, strategic guidance, and mentorship to help businesses navigate challenges and grow effectively.
- Networking Opportunities: Investors can open doors to a wide network of industry contacts, potential partners, and customers, which can be crucial for business growth.
- Credibility and Validation: Securing venture capital can enhance a company's reputation, signaling to the market that the business has strong potential and is backed by experienced investors.
- Flexible Repayment Terms: Unlike loans, venture capital does not require immediate repayment, reducing financial pressure on the business during its early stages.
Disadvantages of Venture Capital
While venture capital has its benefits, it also comes with certain drawbacks. Here are the main disadvantages:
- Equity Dilution: Venture capitalists typically require equity in exchange for funding, which means founders may lose a significant portion of ownership and control over their company.
- High Expectations: Investors often expect high returns on their investment, which can create pressure to achieve rapid growth and profitability, sometimes at the expense of long-term sustainability.
- Loss of Autonomy: Venture capitalists may demand a say in business decisions, potentially limiting the founder's ability to run the company as they see fit.
- Risk of Misalignment: If the goals of the investors and founders do not align, it can lead to conflicts and hinder the company's progress.
- Lengthy and Complex Process: Securing venture capital can be time-consuming and requires extensive preparation, including detailed business plans and financial projections.
When to Consider Venture Capital
Venture capital is not suitable for every business. Here are scenarios where it might be a good fit:
- High-Growth Potential: If your business operates in a high-growth industry and has the potential to scale rapidly, venture capital can provide the necessary resources.
- Innovative Products or Services: Companies with unique, innovative offerings that require significant upfront investment may benefit from venture capital.
- Need for Expertise: If your business lacks industry expertise or strategic guidance, venture capitalists can fill that gap.
- Long-Term Vision: Venture capital is ideal for businesses with a long-term vision that aligns with the investor's goals of achieving substantial returns.
- Limited Access to Traditional Financing: Startups with limited collateral or credit history may find venture capital a viable alternative to traditional loans.
Key Factors to Evaluate Before Seeking Venture Capital
Before pursuing venture capital, consider the following factors to ensure it aligns with your business goals:
- Equity vs. Control: Assess how much equity you are willing to give up and whether you are comfortable sharing control with investors.
- Growth Strategy: Ensure your business has a clear and scalable growth strategy that aligns with the expectations of venture capitalists.
- Investor Fit: Research potential investors to find those who share your vision and can add value beyond just funding.
- Exit Strategy: Understand that venture capitalists typically seek an exit strategy, such as an IPO or acquisition, within a specific timeframe.
- Financial Projections: Prepare detailed financial projections to demonstrate the potential for high returns and justify the investment.
Alternatives to Venture Capital
If venture capital is not the right fit, consider these alternative funding options:
- Bootstrapping: Self-funding your business allows you to retain full control and avoid equity dilution, though it may limit growth potential.
- Angel Investors: Individual investors may provide smaller amounts of capital with less stringent terms compared to venture capitalists.
- Crowdfunding: Platforms like Kickstarter or Indiegogo allow you to raise funds from a large number of people, often in exchange for early access to products or other rewards.
- Bank Loans: Traditional loans can provide funding without giving up equity, though they require repayment with interest and may require collateral.
- Grants and Subsidies: Government or private grants can provide non-repayable funds, particularly for businesses in specific industries or regions.
Frequently Asked Questions from Our Community
What is a major drawback of accepting venture capital?
One of the most significant drawbacks of accepting venture capital is the loss of control over your company. Venture capitalists often require a substantial equity stake in exchange for their investment, which can lead to reduced decision-making power for the founders. Additionally, they may impose specific terms or conditions that align with their financial goals, potentially conflicting with the original vision of the business.
How does venture capital impact company ownership?
Accepting venture capital typically means giving up a portion of your company's ownership. This dilution of equity can affect not only the founders but also early employees who hold stock options. Over time, as more funding rounds occur, the original stakeholders may find their ownership percentage significantly reduced, impacting their influence and potential financial returns.
What are the risks of high expectations from venture capitalists?
Venture capitalists often expect a high return on investment within a relatively short timeframe. This pressure can lead to aggressive growth strategies that may not align with the company's long-term goals or sustainable practices. The focus on rapid scaling can sometimes result in poor decision-making, burnout, or even the failure of the business if the expected growth is not achieved.
Can accepting venture capital limit future funding options?
Yes, accepting venture capital can sometimes limit future funding options. Investors may include clauses in their agreements that restrict the company from seeking additional funding from other sources without their approval. This can create challenges if the company needs to raise more capital later or if the relationship with the initial investors becomes strained. Additionally, future investors may be wary of entering a company with complex existing agreements.
Leave a Reply


Our Recommended Articles