Secondary investments in venture capital refer to the purchase of existing stakes in private companies from early investors or shareholders, rather than investing directly in new funding rounds. This approach allows investors to enter mature startups with proven traction, reducing some of the risks associated with early-stage investments. Secondary markets have gained popularity as they provide liquidity to early backers and employees while offering new investors access to high-growth companies at potentially favorable valuations. This article explores the concept of secondary investments, their unique advantages, and how they contribute to diversifying portfolios and mitigating risks in the dynamic venture capital landscape.
- What Are Secondary Investments in Venture Capital and What Are the Benefits?
- What are secondary investments in venture capital?
- What is the difference between primary and secondary investment in venture capital?
- How do secondary markets benefit investors?
- What benefit to investors does investing in the secondary market have over investing in the primary market?
- Frequently Asked Questions from Our Community
What Are Secondary Investments in Venture Capital and What Are the Benefits?
Secondary investments in venture capital refer to the purchase of existing stakes in private companies or venture capital funds from current investors. These transactions allow investors to buy into companies or funds that are already established, rather than investing directly in new startups. This approach offers unique advantages, such as reduced risk, faster liquidity, and access to mature companies with proven track records.
Understanding Secondary Investments in Venture Capital
Secondary investments involve acquiring shares or interests in private companies or venture capital funds from existing stakeholders. Unlike primary investments, where capital is directly injected into a company, secondary transactions occur between investors. This market has grown significantly as it provides liquidity to early investors and allows new investors to enter at a later stage.
See Also Whats the Difference Between Growth Equity and Venture Capital
Whats the Difference Between Growth Equity and Venture CapitalKey Benefits of Secondary Investments
Secondary investments offer several advantages, including reduced risk due to the maturity of the companies involved, faster liquidity compared to traditional venture capital investments, and the ability to diversify portfolios with established businesses. Additionally, these investments often come with more transparent valuations, as the companies have a track record of performance.
How Secondary Investments Differ from Primary Investments
While primary investments involve funding new startups or early-stage companies, secondary investments focus on acquiring stakes in more mature companies or funds. This distinction means that secondary investors benefit from lower uncertainty and proven business models, whereas primary investors take on higher risk for potentially higher rewards.
Types of Secondary Transactions in Venture Capital
There are two main types of secondary transactions: direct secondaries, where investors buy shares in a specific company, and fund secondaries, where investors purchase interests in a venture capital fund. Both types provide opportunities to invest in established entities, but they differ in terms of structure and focus.
See Also What Are the Best Venture Capital Newsletters?
What Are the Best Venture Capital Newsletters?Risks and Challenges of Secondary Investments
Despite their benefits, secondary investments come with challenges such as valuation complexities, limited availability of opportunities, and potential conflicts of interest between buyers and sellers. Investors must conduct thorough due diligence to mitigate these risks and ensure a successful transaction.
| Aspect | Primary Investments | Secondary Investments |
|---|---|---|
| Stage of Investment | Early-stage companies | Mature companies or funds |
| Risk Level | High | Moderate to Low |
| Liquidity | Long-term | Faster |
| Valuation Transparency | Low | High |

What are secondary investments in venture capital?
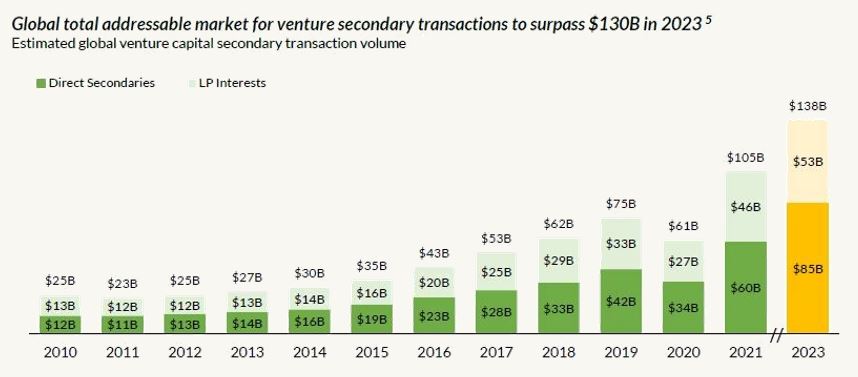
What Are Secondary Investments in Venture Capital?
Secondary investments in venture capital refer to the purchase of existing stakes in private companies or venture capital funds from current investors. These transactions allow early investors, such as limited partners (LPs) or employees, to liquidate their holdings before a company goes public or is acquired. Secondary markets provide liquidity in an otherwise illiquid asset class, enabling investors to buy into or exit positions in private companies.
See Also What Percent of Venture Capital Funds Fail?
What Percent of Venture Capital Funds Fail?- Liquidity for early investors: Secondary investments enable early investors to cash out their stakes without waiting for an IPO or acquisition.
- Access to mature startups: Buyers can invest in established companies with proven track records, reducing some of the risks associated with early-stage investing.
- Diversification of portfolios: Investors can gain exposure to a broader range of private companies through secondary transactions.
How Do Secondary Transactions Work?
Secondary transactions involve the transfer of ownership in private companies or venture capital funds from one party to another. These deals are typically facilitated by specialized brokers or secondary market platforms. The process includes valuation negotiations, due diligence, and legal documentation to ensure a smooth transfer of ownership.
- Valuation: The price is determined based on the company's current performance, growth potential, and market conditions.
- Due diligence: Buyers conduct thorough research to assess the company's financial health and future prospects.
- Legal agreements: Contracts are drafted to formalize the transfer of shares or fund interests.
Who Participates in Secondary Markets?
Secondary markets attract a diverse group of participants, including institutional investors, family offices, high-net-worth individuals, and specialized secondary funds. These players seek opportunities to invest in or exit private companies at different stages of their growth.
- Institutional investors: Pension funds, endowments, and sovereign wealth funds often participate to diversify their portfolios.
- Secondary funds: Dedicated funds focus exclusively on acquiring secondary stakes in private companies or venture capital funds.
- Individual investors: High-net-worth individuals may participate through platforms offering access to secondary transactions.
Benefits of Secondary Investments
Secondary investments offer several advantages, including reduced risk, faster returns, and access to high-quality assets. These benefits make them an attractive option for investors looking to balance their portfolios.
See Also What Are Alternatives to Venture Capital?
What Are Alternatives to Venture Capital?- Reduced risk: Investing in more mature companies lowers the uncertainty associated with early-stage ventures.
- Faster returns: Secondary investments often provide quicker liquidity compared to traditional venture capital.
- Access to premium assets: Buyers can acquire stakes in high-performing companies that are otherwise difficult to access.
Challenges of Secondary Investments
Despite their advantages, secondary investments come with challenges such as pricing complexity, limited transparency, and regulatory hurdles. These factors can make secondary transactions more complicated than primary investments.
- Pricing complexity: Valuing private companies can be subjective and challenging due to limited public data.
- Limited transparency: Secondary markets often lack the same level of information as public markets.
- Regulatory hurdles: Compliance with securities laws and transfer restrictions can complicate transactions.
What is the difference between primary and secondary investment in venture capital?

What is Primary Investment in Venture Capital?
Primary investment in venture capital refers to the initial funding provided directly to a startup or company in exchange for equity. This type of investment is typically made during the early stages of a company's development, such as seed rounds or Series A funding. Key characteristics include:
- Direct funding: Investors provide capital directly to the company.
- Equity stake: Investors receive shares in the company in return for their investment.
- High risk, high reward: Early-stage investments carry significant risk but offer the potential for substantial returns if the company succeeds.
What is Secondary Investment in Venture Capital?
Secondary investment involves purchasing existing shares from early investors, employees, or other stakeholders rather than directly funding the company. This type of investment typically occurs in later stages when the company has already established some level of success. Key characteristics include:
- Indirect funding: Capital flows to existing shareholders, not the company itself.
- Liquidity for early investors: Provides an exit opportunity for early backers or employees holding equity.
- Lower risk: Since the company is more established, the risk is generally lower compared to primary investments.
Key Differences Between Primary and Secondary Investments
The primary distinction lies in the flow of capital and the stage of the company. Here are the main differences:
- Capital allocation: Primary investments fund the company directly, while secondary investments fund existing shareholders.
- Stage of investment: Primary investments occur in early stages, whereas secondary investments happen in later stages.
- Risk profile: Primary investments are riskier due to the company's unproven status, while secondary investments are less risky as the company is more established.
Advantages of Primary Investments
Primary investments offer unique benefits for investors willing to take on higher risk. These include:
- Higher potential returns: Early-stage investments can yield significant profits if the company grows successfully.
- Influence on company direction: Investors often gain a say in strategic decisions due to their equity stake.
- Long-term growth opportunities: Investors can benefit from the company's growth over time.
Advantages of Secondary Investments
Secondary investments provide distinct advantages, particularly for risk-averse investors. These include:
- Reduced risk: Investing in more established companies lowers the likelihood of failure.
- Faster liquidity: Secondary markets allow investors to buy and sell shares more easily.
- Access to proven companies: Investors can invest in companies with a track record of success.
How do secondary markets benefit investors?
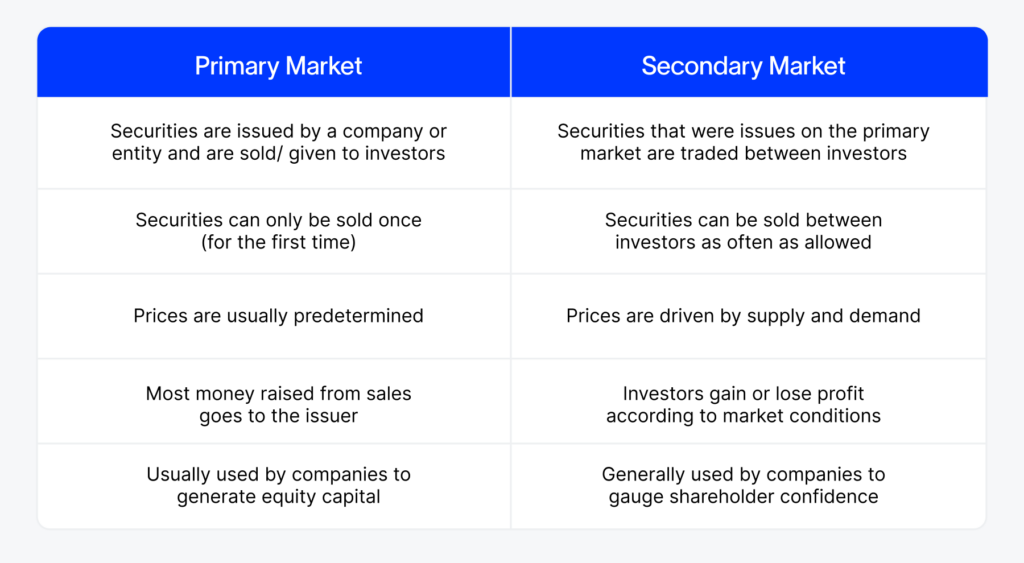
Enhanced Liquidity for Investors
Secondary markets provide investors with the ability to quickly buy or sell securities, ensuring that their investments are not locked in for extended periods. This liquidity is crucial for several reasons:
- Flexibility: Investors can easily convert their holdings into cash when needed, allowing them to respond to personal financial needs or market opportunities.
- Price Discovery: The continuous trading in secondary markets helps in determining the fair market value of securities based on supply and demand.
- Reduced Risk: The ability to exit investments quickly reduces the risk of holding illiquid assets, which can be difficult to sell without significant loss.
Diversification Opportunities
Secondary markets offer a wide range of investment options, enabling investors to diversify their portfolios effectively. This diversification is beneficial because:
- Risk Management: By spreading investments across various sectors and asset classes, investors can mitigate the impact of poor performance in any single investment.
- Access to Different Markets: Investors can participate in both domestic and international markets, gaining exposure to different economic conditions and growth opportunities.
- Variety of Instruments: From stocks and bonds to derivatives and ETFs, secondary markets provide a plethora of financial instruments to suit different investment strategies.
Improved Market Efficiency
Secondary markets contribute to the overall efficiency of financial markets by facilitating the flow of information and capital. This efficiency is achieved through:
- Transparency: Continuous trading and real-time price updates ensure that all market participants have access to the same information, reducing information asymmetry.
- Competition: The presence of numerous buyers and sellers fosters competitive pricing, ensuring that securities are traded at their true market value.
- Lower Transaction Costs: High liquidity and competition in secondary markets often lead to lower bid-ask spreads and reduced trading costs for investors.
Access to Historical Data and Trends
Investors in secondary markets can leverage historical data and trends to make informed decisions. This access is valuable because:
- Performance Analysis: Historical price movements and trading volumes help investors analyze the performance of securities over time.
- Pattern Recognition: Identifying trends and patterns can assist in predicting future price movements and making strategic investment choices.
- Benchmarking: Investors can compare the performance of their investments against market indices or peer securities to assess relative performance.
Opportunities for Capital Gains
Secondary markets provide investors with the potential to earn capital gains through the appreciation of security prices. This potential is driven by:
- Market Growth: As companies grow and their earnings increase, the value of their securities often rises, leading to capital gains for investors.
- Speculative Trading: Investors can capitalize on short-term price fluctuations to buy low and sell high, generating profits from market volatility.
- Dividend Reinvestment: Reinvesting dividends in secondary markets can compound returns over time, enhancing the overall growth of the investment portfolio.
What benefit to investors does investing in the secondary market have over investing in the primary market?

Liquidity and Flexibility
Investing in the secondary market offers investors greater liquidity and flexibility compared to the primary market. This is because:
- Shares or securities can be bought and sold at any time during market hours, allowing investors to exit or enter positions quickly.
- There is no lock-in period, unlike in the primary market where investors may have to wait for the IPO to conclude or for the stock to list.
- The ability to trade frequently enables investors to respond to market changes and adjust their portfolios as needed.
Price Transparency
The secondary market provides price transparency, which is a significant advantage for investors. This is evident because:
- Prices are determined by supply and demand, reflecting real-time market sentiment.
- Investors can access historical price data and trends to make informed decisions.
- Unlike the primary market, where prices are fixed during the issuance, secondary market prices fluctuate, offering opportunities for profit maximization.
Diverse Investment Options
The secondary market offers a wider range of investment options compared to the primary market. This includes:
- Access to a variety of stocks, bonds, ETFs, and other securities already in circulation.
- The ability to invest in companies that have already proven their market viability, reducing the risk associated with new issuances.
- Opportunities to diversify portfolios across industries, sectors, and geographies.
Lower Risk
Investing in the secondary market generally involves lower risk compared to the primary market. This is due to:
- The availability of historical performance data, which helps investors assess the stability and growth potential of a security.
- Reduced uncertainty, as companies listed in the secondary market have already gone through the IPO process and are subject to regulatory scrutiny.
- The ability to set stop-loss orders and other risk management tools to protect investments.
Market Accessibility
The secondary market is more accessible to individual investors than the primary market. This is because:
- Investors do not need to meet high minimum investment requirements, which are often associated with IPOs.
- Trading platforms and brokerage accounts make it easy for retail investors to participate in the secondary market.
- There are no restrictions on the number of shares an investor can buy or sell, unlike in the primary market where allocations may be limited.
Frequently Asked Questions from Our Community
What are secondary investments in venture capital?
Secondary investments in venture capital refer to the purchase of existing stakes in private companies or venture capital funds from current investors. These transactions typically occur when early investors, such as limited partners (LPs) or employees, want to liquidate their holdings before the company goes public or is acquired. Unlike primary investments, where capital is directly invested into a company, secondary investments involve buying shares or interests that have already been issued. This market has grown significantly as it provides liquidity in an otherwise illiquid asset class.
What are the benefits of secondary investments in venture capital?
Secondary investments offer several advantages for both buyers and sellers. For buyers, they provide access to established companies or funds with proven track records, reducing the risk associated with early-stage investments. Sellers benefit by gaining liquidity without waiting for an exit event like an IPO or acquisition. Additionally, secondary transactions often occur at a discount, allowing buyers to acquire stakes at lower valuations. This market also enables portfolio diversification and shorter investment horizons compared to traditional venture capital investments.
Who typically participates in secondary venture capital transactions?
Secondary venture capital transactions involve a variety of participants, including institutional investors, family offices, specialized secondary funds, and high-net-worth individuals. Sellers are often early investors, such as venture capital funds looking to rebalance their portfolios or employees with equity in startups. Buyers are typically entities seeking exposure to mature startups or funds without the long lock-up periods associated with primary investments. The growing interest in this market has also attracted new players, such as hedge funds and private equity firms, further expanding its scope.
What risks are associated with secondary investments in venture capital?
While secondary investments offer numerous benefits, they also come with risks. One major risk is the lack of transparency in pricing, as private company valuations can be subjective and vary widely. Buyers may also face challenges in conducting thorough due diligence, as access to company information may be limited. Additionally, the illiquid nature of these assets means that exiting a position can be difficult if market conditions change. Finally, regulatory and legal complexities can arise, particularly when dealing with cross-border transactions or employee stock options.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles