Series 1 financing, often referred to as Series A in some contexts, represents a critical stage in a startup's growth journey. It is typically the first significant round of venture capital funding, aimed at scaling operations, refining products, and expanding market reach. At this stage, investors evaluate the company's potential for long-term success, focusing on metrics like traction, team strength, and market opportunity. Series 1 funding allows startups to transition from early-stage development to a more structured growth phase, often marking a turning point in their evolution. Understanding this funding stage is essential for entrepreneurs and investors alike, as it sets the foundation for future success.
What Does a Series 1 Financing/ Funding Mean?
Series 1 financing, also known as Series A funding in some contexts, refers to the first significant round of venture capital financing for a startup. This stage typically occurs after the seed funding phase and is aimed at helping the company scale its operations, develop its product further, and expand its market reach. Investors in this round are usually venture capital firms, angel investors, or institutional investors who believe in the startup's potential for growth and profitability.
1. What is the Purpose of Series 1 Financing?
The primary purpose of Series 1 financing is to provide the startup with the necessary capital to scale its operations and achieve significant milestones. This funding is often used to hire key talent, enhance product development, expand into new markets, and increase marketing efforts. It is a critical step for startups transitioning from the early-stage to the growth-stage.
See Also What Are Differences Between Venture Series a B C D and Seed Rounds
What Are Differences Between Venture Series a B C D and Seed Rounds2. Who Participates in Series 1 Financing?
Participants in Series 1 financing typically include venture capital firms, angel investors, and sometimes corporate investors. These investors provide capital in exchange for equity stakes in the company. The involvement of reputable investors can also lend credibility to the startup, making it easier to attract future funding.
3. How is Series 1 Financing Structured?
Series 1 financing is usually structured as an equity round, where investors receive preferred shares in the company. These shares often come with specific rights, such as liquidation preferences and anti-dilution protections. The terms of the financing are outlined in a term sheet, which is negotiated between the startup and the investors.
4. What are the Key Metrics Investors Look For?
Investors in Series 1 financing typically look for startups with a proven business model, strong traction, and a clear path to profitability. Key metrics may include monthly recurring revenue (MRR), customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value (LTV), and growth rate. Demonstrating a large addressable market and a scalable product is also crucial.
See Also How Much Does a Venture Capital Associate Earn Per Year?
How Much Does a Venture Capital Associate Earn Per Year?5. What are the Risks and Challenges of Series 1 Financing?
While Series 1 financing can provide significant capital, it also comes with risks and challenges. Startups may face dilution of ownership, pressure to meet investor expectations, and the challenge of managing rapid growth. Additionally, the process of securing funding can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
| Key Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Series 1 Financing | The first significant round of venture capital financing for a startup. |
| Venture Capital Firms | Institutions that provide capital to startups in exchange for equity. |
| Preferred Shares | Equity shares with specific rights and preferences over common shares. |
| Term Sheet | A document outlining the terms and conditions of the investment. |
| Liquidation Preferences | Rights that give investors priority in receiving proceeds in the event of a liquidation. |
What is series 1 in funding?
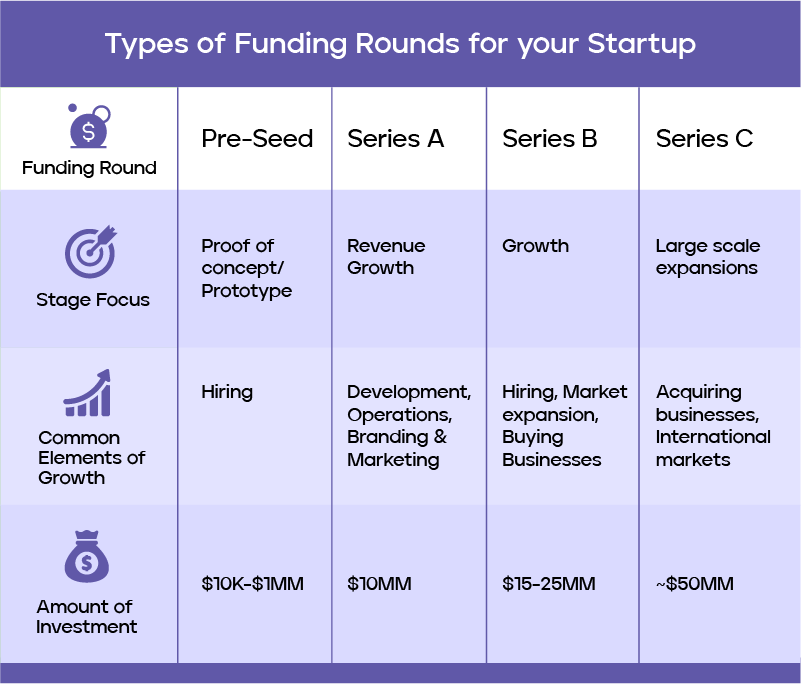
What is Series 1 Funding?
Series 1 funding, often referred to as Series A funding in some contexts, is the first significant round of venture capital financing for a startup. It typically follows the seed funding stage and is aimed at scaling the business. This stage is crucial for startups as it allows them to expand their operations, develop their product further, and grow their customer base. Investors in Series 1 funding are usually venture capital firms, and they expect a higher level of business maturity compared to seed-stage investments.
See Also How to Find a Vc in Dubai
How to Find a Vc in DubaiKey Characteristics of Series 1 Funding
Series 1 funding has distinct characteristics that set it apart from other funding stages:
- Higher Investment Amounts: Series 1 funding typically involves larger sums of money compared to seed funding, often ranging from $2 million to $15 million.
- Equity Exchange: In exchange for funding, investors receive equity in the company, usually between 10% to 30%.
- Focus on Growth: The primary goal of Series 1 funding is to scale the business, including expanding the team, entering new markets, and increasing production capacity.
Who Participates in Series 1 Funding?
Series 1 funding involves several key players:
- Venture Capital Firms: These are the primary investors in Series 1 funding, providing the necessary capital in exchange for equity.
- Angel Investors: Some high-net-worth individuals may also participate, especially if they have been involved in earlier funding rounds.
- Startup Founders: Founders play a crucial role in pitching their business and negotiating terms with investors.
How to Prepare for Series 1 Funding
Preparing for Series 1 funding requires careful planning and execution:
See Also Are there any reasons why a startup would not want to go through TechStars?
Are there any reasons why a startup would not want to go through TechStars?- Develop a Strong Business Plan: A detailed business plan that outlines growth strategies, market analysis, and financial projections is essential.
- Build a Solid Team: Investors look for a capable and experienced team that can execute the business plan effectively.
- Show Traction: Demonstrating market traction through metrics like user growth, revenue, and customer retention is critical to attracting investors.
Risks and Challenges in Series 1 Funding
While Series 1 funding offers significant opportunities, it also comes with risks:
- Equity Dilution: Founders may have to give up a significant portion of their equity, reducing their ownership stake.
- Increased Pressure: With more capital comes higher expectations from investors, leading to increased pressure to deliver results.
- Market Risks: Expanding operations and entering new markets can be risky, especially if the market conditions are unfavorable.
Is Series A or B better?

What is Series A Funding?
Series A funding is the first significant round of venture capital financing for a startup. It typically follows the seed funding stage and is used to scale the business. Key aspects include:
See Also How Do I Get a Meeting With a Venture Capitalist?
How Do I Get a Meeting With a Venture Capitalist?- Purpose: To scale operations, expand the team, and refine the product.
- Investors: Usually involves venture capital firms and angel investors.
- Valuation: Startups are often valued between $10 million and $30 million.
What is Series B Funding?
Series B funding is the next stage after Series A, aimed at taking the business to the next level. It focuses on:
- Growth: Expanding market reach and increasing customer base.
- Investors: Often includes more institutional investors and venture capital firms.
- Valuation: Companies are typically valued between $30 million and $60 million.
Key Differences Between Series A and Series B
Understanding the differences between Series A and Series B can help in deciding which is better for a startup:
- Stage of Business: Series A is for early-stage scaling, while Series B is for established growth.
- Funding Amount: Series B usually involves larger funding amounts compared to Series A.
- Investor Expectations: Series B investors expect more proven metrics and growth potential.
Advantages of Series A Funding
Series A funding offers several advantages for startups:
- Initial Scaling: Provides the necessary capital to scale operations and refine the product.
- Investor Support: Early investors often provide mentorship and strategic guidance.
- Valuation Boost: Helps in achieving a higher valuation for future funding rounds.
Advantages of Series B Funding
Series B funding comes with its own set of benefits:
- Expansion: Enables significant market expansion and customer acquisition.
- Stability: Companies are more stable and have proven business models.
- Larger Investments: Attracts larger investments from more established investors.
How much do you get paid for Series A funding?

What is Series A Funding?
Series A funding is the first significant round of venture capital financing for a startup after the initial seed stage. It typically involves raising funds from venture capital firms or angel investors to scale operations, develop products, and expand the team. The amount raised in Series A can vary widely depending on the industry, market potential, and the startup's growth trajectory.
- Purpose: Series A funding is used to scale the business, refine the product, and enter new markets.
- Investors: Typically involves venture capital firms, angel investors, or institutional investors.
- Valuation: The startup's valuation is determined based on its potential, traction, and market size.
How Much Do Founders Get Paid in Series A Funding?
Founders' salaries during Series A funding are generally modest compared to the overall funding raised. The focus is on reinvesting the funds into the business. However, founders may receive a salary to cover living expenses, which is often negotiated with investors.
- Salary Range: Founders typically earn between $70,000 and $150,000 annually during Series A.
- Negotiation: Salaries are often negotiated based on the startup's stage, location, and funding amount.
- Equity: Founders usually retain a significant portion of equity, which can be more valuable in the long term.
How Much Do Employees Get Paid in Series A Funding?
Employee compensation during Series A funding varies depending on the role, experience, and location. Startups often offer a mix of salary and equity to attract top talent while conserving cash.
- Salary: Employees may earn between $50,000 and $120,000 annually, depending on their role.
- Equity: Equity packages are common, with employees receiving stock options or restricted stock units (RSUs).
- Benefits: Startups may offer additional benefits like health insurance, flexible work hours, or remote work options.
How Much Do Investors Get Paid in Series A Funding?
Investors in Series A funding do not receive direct payments but instead acquire equity in the startup. Their return on investment comes from the startup's future growth, such as through an acquisition or IPO.
- Equity Stake: Investors typically receive between 10% and 30% equity in the startup.
- Board Seats: Investors may secure board seats to influence the company's direction.
- Return on Investment: Investors aim for a significant return, often targeting a 10x to 20x multiple on their initial investment.
What Factors Influence Compensation in Series A Funding?
Several factors influence how much individuals get paid during Series A funding, including the startup's valuation, industry, location, and the amount raised.
- Valuation: Higher valuations can lead to higher salaries and larger equity stakes.
- Industry: Tech startups often offer higher compensation compared to other industries.
- Location: Salaries vary based on the cost of living in the startup's location.
- Funding Amount: Larger funding rounds may allow for more competitive compensation packages.
What is series I funding?

What is Series I Funding?
Series I funding refers to the initial stage of investment in a startup or company, typically provided by angel investors, venture capitalists, or seed funds. This funding is crucial for early-stage companies to develop their product, conduct market research, and build a team. The investment is often exchanged for equity in the company, giving investors a stake in its future success.
- Purpose: Series I funding is primarily used to validate the business idea and achieve initial milestones.
- Investors: Common investors include angel investors, venture capital firms, and sometimes friends and family.
- Equity Exchange: Investors receive shares in the company in return for their financial support.
How Does Series I Funding Work?
Series I funding works by providing capital to startups in exchange for ownership stakes. Investors evaluate the potential of the business and its team before committing funds. The process typically involves:
- Pitching: Founders present their business plan to potential investors.
- Valuation: The company’s worth is assessed to determine the equity share for investors.
- Agreement: Terms are negotiated, and legal documents are signed to formalize the investment.
Key Benefits of Series I Funding
Series I funding offers several advantages for startups, including:
- Capital Injection: Provides the necessary funds to kickstart operations and product development.
- Expertise: Investors often bring valuable industry knowledge and mentorship.
- Networking: Access to the investor’s network can open doors to partnerships and future funding rounds.
Challenges of Series I Funding
While beneficial, Series I funding also comes with challenges, such as:
- Equity Dilution: Founders may lose a significant portion of ownership.
- High Expectations: Investors expect a return on their investment, adding pressure to perform.
- Time-Consuming: Securing funding requires extensive preparation and negotiation.
How to Secure Series I Funding
To successfully secure Series I funding, startups should:
- Prepare a Strong Pitch: Clearly articulate the business idea, market potential, and growth strategy.
- Build a Prototype: Demonstrating a working product can increase investor confidence.
- Network: Attend industry events and leverage connections to meet potential investors.
Frequently Asked Questions from Our Community
What is Series 1 Financing?
Series 1 Financing refers to the first significant round of venture capital funding that a startup or early-stage company raises from external investors. This stage typically occurs after the company has demonstrated some level of market validation, such as a working product, initial revenue, or a growing customer base. The funds raised during Series 1 Financing are often used to scale operations, expand the team, invest in marketing, and further develop the product or service. It is a critical milestone that helps startups transition from the seed stage to a more established phase of growth.
How does Series 1 Financing differ from Seed Funding?
Series 1 Financing is distinct from Seed Funding in terms of the company's stage of development and the amount of capital raised. While Seed Funding is typically used to validate an idea, build a prototype, or conduct market research, Series 1 Financing is aimed at scaling a business that has already shown potential. The funding amounts in Series 1 are usually larger, and the investors involved are often institutional venture capital firms rather than angel investors or friends and family. This round also involves more formalized terms and valuations compared to the earlier seed stage.
Who typically invests in Series 1 Financing?
Series 1 Financing is usually led by institutional investors such as venture capital firms, which specialize in funding high-growth startups. These firms bring not only capital but also expertise, mentorship, and valuable industry connections. In some cases, angel investors or corporate venture arms may also participate in this round. The involvement of reputable investors during Series 1 can significantly enhance the company's credibility and attract further interest from other investors or stakeholders.
What are the key terms to consider in Series 1 Financing?
During Series 1 Financing, several key terms are negotiated between the company and the investors. These include the valuation of the company, which determines how much equity the investors will receive in exchange for their capital. Other important terms include liquidation preferences, which outline how proceeds will be distributed in the event of a sale or liquidation, and board seats, which may be granted to investors to allow them to influence company decisions. Additionally, anti-dilution provisions and vesting schedules for founders and employees are often discussed to ensure alignment of interests between all parties involved.
Leave a Reply


Our Recommended Articles